Question
Question: Let a total charge 2Q be distributed in a sphere of radius R, with the charge density given by p(r) ...
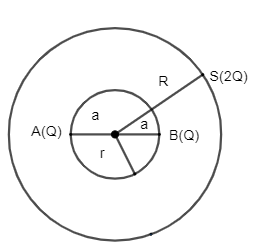
Let a total charge 2Q be distributed in a sphere of radius R, with the charge density given by p(r) = kr, where r is the distance from the centre two charges A and B of –Q each are placed on diametrically opposite points, at equal distance a form the center. If A and B do not experience force, then:
A. a=2413RB. a=3RC. a=8−41RD. a=2−41R
Solution
In order to find solution of this question force on A due to B must be equal to force on A due to sphere S to do so we have to find electric field on AB in order to do it we have to draw gauss’s surface inside a sphere S with radius r.
Formula used: ∮E.dA=ε0Qin
F=r2kq1q2
Complete answer:
In order to find a solution and equilibrium condition force on A due to B is equal to force on A due to S since A and B are at equal distance and have equal charge Q.
FAB=FAS......(1)
Now force on A due to B
FAB=4πε01(2a)2Q2.....(2)
FAB = electric force between A and B
k =4πε01= proportionality constant
Q = charge
a = radius or distance between two charges.
Force due to S and A
FAS=E.Q.....(3)
First we have to find electric field E we will take gauss’s surface to find electric field on A and B now,
∮E.dA=ε0Qin
E= Electric field
dA = area
Qin= Charge inside a sphere
ε0 = permittivity
Electric field is constant hence
E∮dA=0∫rε0ρdv
Now we know that area of the radius r circle is
A=4πr2
And it is given in question that ρ=kr
Now
⇒E.4πr2=0∫rkrε04πr2dr⇒E.4πr2=ε04πk(4r4)∴E=4ε0kr2....(4)
Now we have to find k in order to do it we will use the below equation
Charge on whole sphere
⇒o∫2QdQ=o∫Rρdv⇒2Q=o∫Rkr4πr2dr⇒2Q=k4π4R4∴k=πR42Q
Now substitute the value of k in equation (4)
E=2πε0R4Qr2
From figure we can put r = a
E=2πε0R4Qa2...(5)
Now put all the values in equation (1)
⇒FAB=FAS⇒4πε01(2a)2Q2=E.Q
⇒4πε01(4a)2Q2=2πε0R4Q.a2×Q
⇒16a21=2R4a2⇒a4=162R4⇒a4=81R4∴a=8−41R
Hence the correct option is (c).
Note:
In this question we have to consider both the charge A and B inside the sphere if we consider them outside the sphere the solution could lead us to the wrong answer or solution.
