Question
Question: Let a focal chord of the parabola \({{y}^{2}}=16x\) cuts it at points \(\left( f,g \right)\) and \(\...
Let a focal chord of the parabola y2=16x cuts it at points (f,g) and (h,k). Then f.h is:
A. -8
B. -16
C. 16
D. None of these
Solution
We here need to find f.h , i.e. the product of the x-coordinates of the extremities of the focal chord of the given parabola. For this, we will first write the given coordinates in the parametric form and, i.e. (at12,2at1) and (at22,2at2) and hence write the product in the parametric form. Then we will use the property of t1t2=−1 where t1 and t2 are the parameters for the extremities of the focal chord. We will then put this value in the required product and hence we will get our result.
Complete step-by-step solution
Now, we have been given the two points the focal chord of the parabola y2=16x passes through. A focal chord of a parabola is the chord, which passes through its focus.
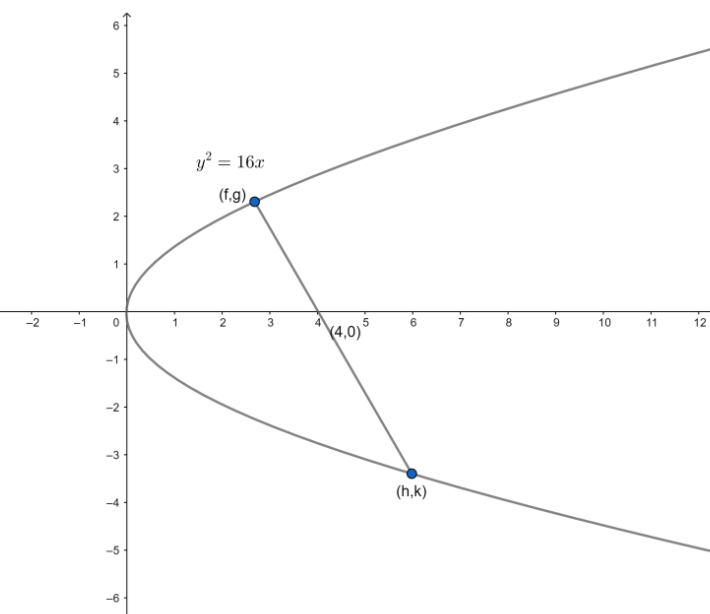
The parabola y2=16x is in the form of y2=4ax where the focus is (a,0) . thus, we can write the given parabola as:
y2=16x⇒y2=4.4x
Thus, for the given parabola, a=4
Now, any point on a parabola y2=4ax is given by (at2,2at) where ‘t’ is a parameter.
As mentioned above, here a=4
Thus, we can take the given points (f,g) and (h,k) as (4t12,8t1) and (4t22,8t2) respectively where ′t1′ and ′t2′ are two different parameters.
Thus, we get:
f=4t12
h=4t22
So we can get f.h as by multiplying these both.
Thus, we get:
f.h=4t12.4t22⇒f.h=16t12t22
⇒f.h=16(t1t2)2 ……(i)
Now, we know that if the focal chord of a parabola of the type y2=4ax passes through the points (at12,2at1) and (at22,2at2) then the relation between the points is given by:
t1t2=−1
Thus, by putting this value, we can find the value of f.h
Now, putting this value in equation (i) we get:
f.h=16(t1t2)2⇒f.h=16(−1)2⇒f.h=16(1)⇒f.h=16
Thus option (C) is the correct option.
Note: We have obtained the result t1t2=−1 by the following method:
In the given figure, we have a parabola y2=4ax with the focus at S. The extremities of the chord are P and Q.
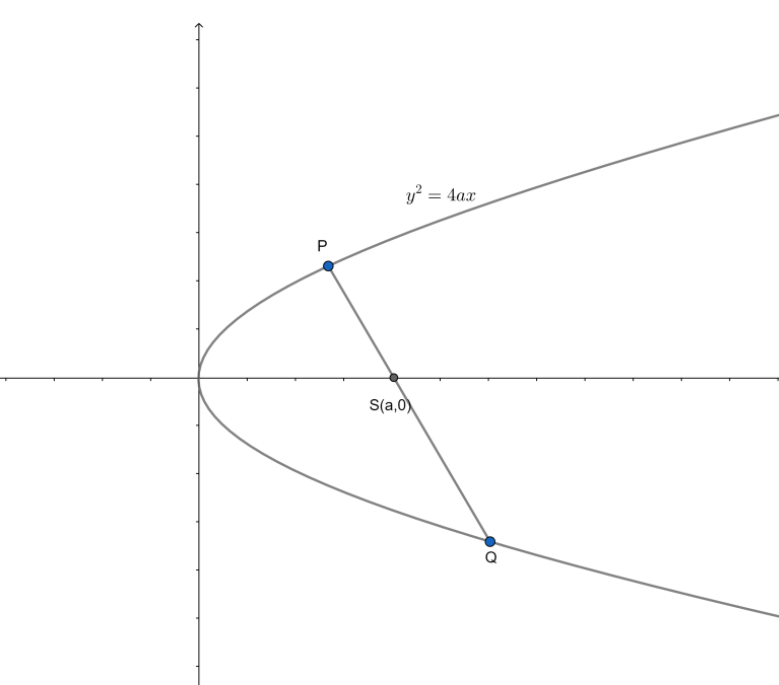
Let the point P be (at12,2at1) and let the point Q be (at22,2at2).
Hence, the equation through point P and Q will be:
y−2at1=at22−at122at2−2at1(x−at12)y−2at1=t2+t12(x−at12)
Now, this line passes through the focus, i.e. S (a,0)
Putting this point in the equation of the chord we get:
