Question
Question: Learning is related to which part of the human brain? (a) Medulla oblongata (b) Hypothalamus (...
Learning is related to which part of the human brain?
(a) Medulla oblongata
(b) Hypothalamus
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Cerebellum
Solution
The part of the human brain to which learning is related is located in the anterior portion of the brain. Its surface is greatly folded into deep grooves and ridges. Along with learning, it also controls various voluntary actions of humans such as the coordinated movement of our body.
Complete answer:
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and controls voluntary actions, speech, thought, and memory. It is divided into two halves i.e. right and left cerebral hemispheres. The outer portion is called the cerebral cortex which contains deep grooves or sulci.
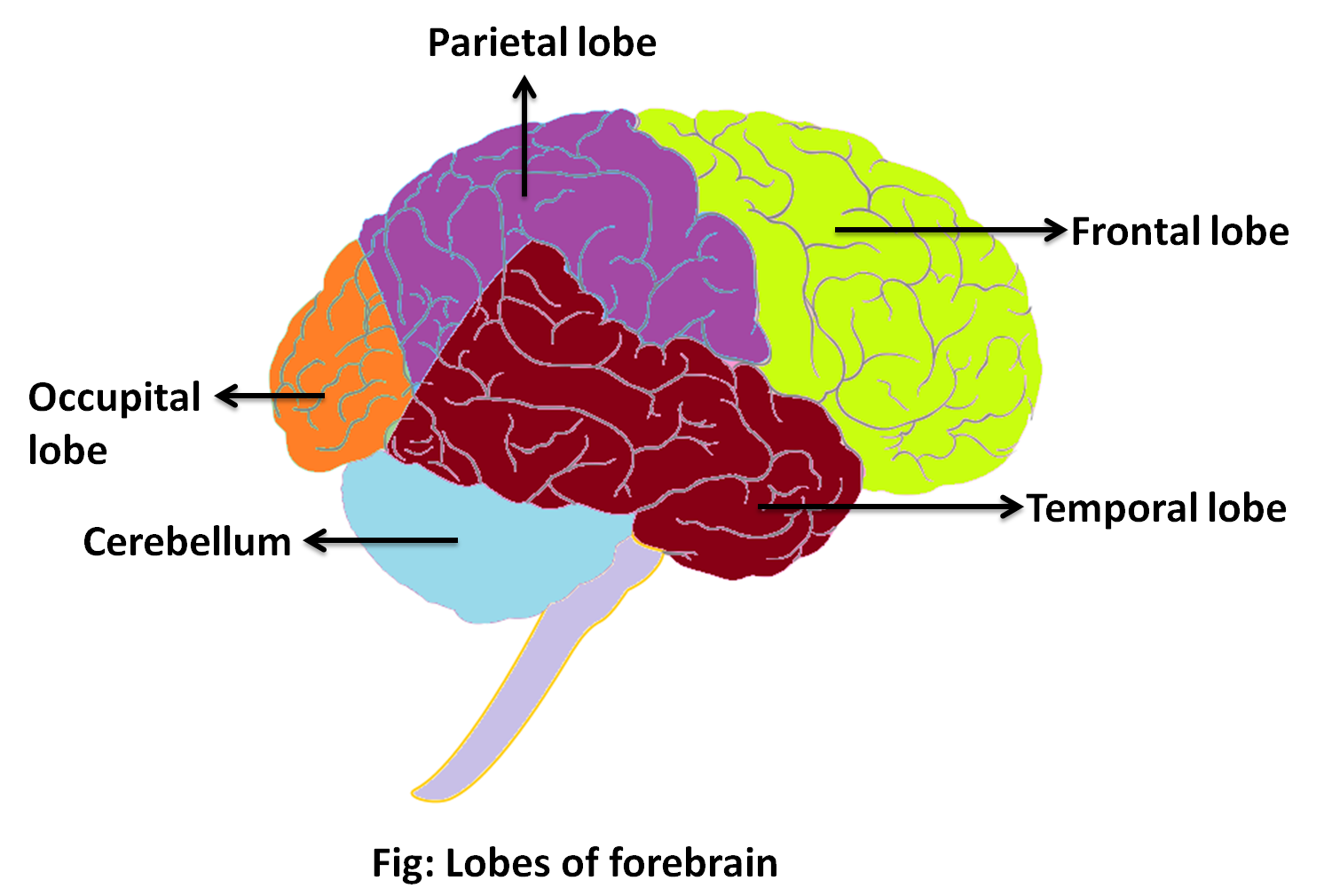
The cerebrum is composed of two cerebral hemispheres, which are further divided into four lobes:
| Lobe | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal lobe | Occupies the front portion of the brain. | Responsible for voluntary movement, decision making, speech output, certain aspects of mood, behaviour, memory, and personality. |
| Parietal lobe | Found behind the frontal lobe. | Processes sensory information such as pain, taste, temperature, and touch. Processing information about numbers, environment. |
| Temporal lobe | Situated at each side of the brain. | Process memory, auditory information, language, speech, smell, and emotion. |
| Occipital lobe | Present at the back of the brain. | Processes visual information, shape, and colour. |
Note:
Hypothalamus, which is a part of the forebrain, deals with water balance in the body, behavioural patterns of sex, sleep, stress, emotions, etc. It also regulates the release of pituitary hormones.
Medulla oblongata and cerebellum are present in the hindbrain. The cerebellum (the second largest part of the rain) is in the bottom part of the head and back of it. Its functions involve balancing and coordinating rapid muscular activities.
Medulla oblongata receives and integrates signals from the spinal cord and brain. It deals with the control of heart rate, breathing, salivation as well as some involuntary movements.
