Question
Question: l-chorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives: (A) 1-butene (B) 1-butanol (C) 2-butane...
l-chorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives:
(A) 1-butene
(B) 1-butanol
(C) 2-butane
(D) 2-butanol
Solution
In alkenes, the molecule contains the double bond between the adjacent carbon atoms. The alkenes can be synthesized from the haloalkanes. Haloalkanes are treated with the potassium hydroxide KOH . The β hydrogen atom shifts its bonds and forms the double bond followed by the removal of the halogen atom at the α position. The reaction contains the removal of hydrogen and halogen, thus the reaction is known as dehydrohalogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first start the answer by writing the chemical reaction. So the chemical reaction goes as follows:
CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl !! !! alcoholic KOH CH3CH2CH = CH2
In the above reaction, alcoholic KOH plays the role of a dehydrohalogenation agent. The alcoholic KOH reacts with an alkyl halide and an alkene is formed as the product of the chemical reaction.
The product that is formed consists of 4 carbon atoms and as we can see there is a double bond that is present between the first and the second carbon atoms. So, the name of the compound will be 1-butene.
The mechanism is as shown below:
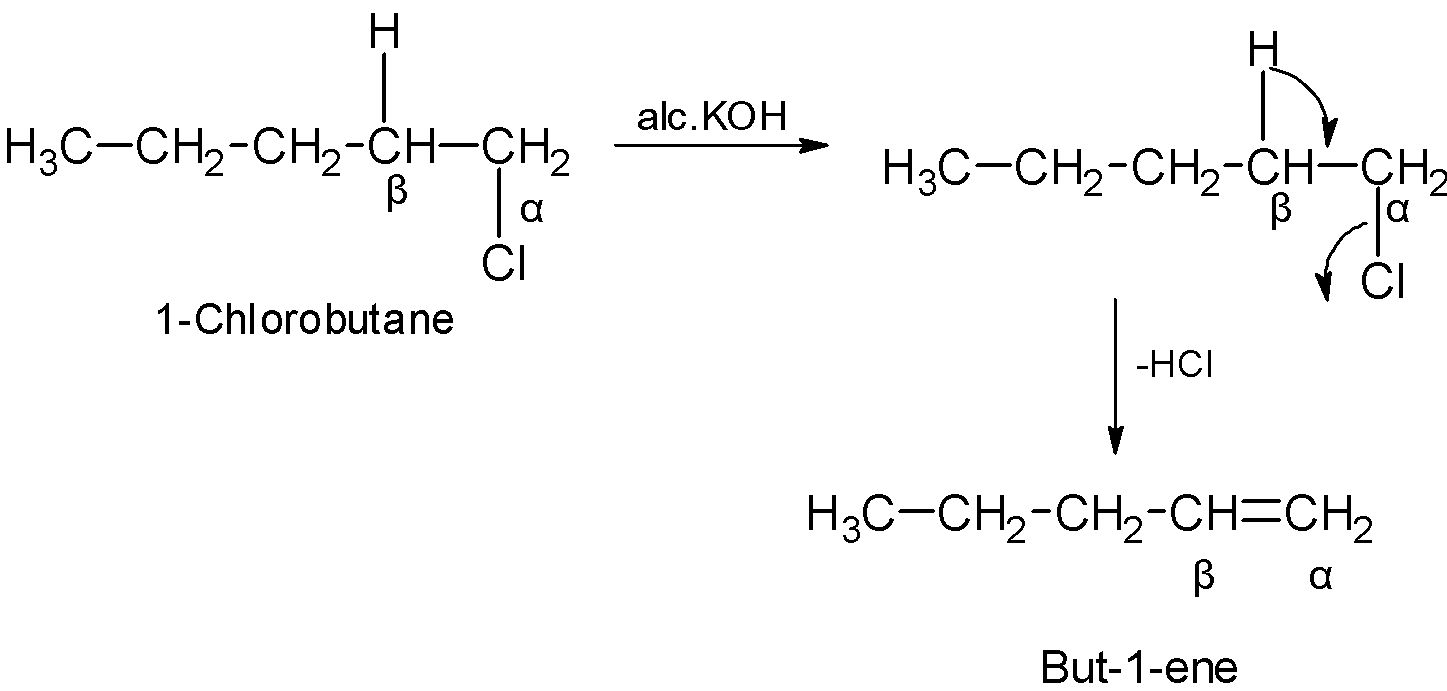
The answer to the question which is 1-butene is an organic compound that is highly flammable and is a highly condensed gas. 1-butene is soluble in ether and alcohol but is not soluble in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
By alcoholic solution, as mentioned in the answer, we mean a solution which is a mixture of water and ethanol, which is used as a solvent. Substances that contain sugar can be fermented using this alcoholic solution.
Note: Alcoholic potash that is used in the chemical reaction mentioned above is a very strong base. Alcoholic potash or as we know KOH dissolves in water to give RO− ions. Alcohol abstracts the hydrogen which results in the formation of elimination in the reaction.
