Question
Question: KI in acetone, undergoes \({{S}_{N}}2\) reaction with each of P, Q, R and S. the rates of the reacti...
KI in acetone, undergoes SN2 reaction with each of P, Q, R and S. the rates of the reaction vary as _____.
P > Q > R > S
S > P > R > Q
Q > R > P> S
R > P > S > Q
Solution
SN2 Reaction are nucleophilic substitution reaction, it involves the attack of a positively charged or a partially positively charged atom or group by a nucleophile. Nucleophiles are the species which are rich in electrons; they can donate an electron pair.
Complete step by step answer:
- SN2 Reaction follows the second order kinetics and it is a single step reaction. The rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of the substrate and nucleophile. There is a formation of a single transition state in SN2 reaction.
- SN2 Reaction leads to a back-side attack, which leads to the inversion of stereochemistry of the carbon atom, here a complete inversion of configuration takes place.
Mechanism of SN2 reaction is mentioned below:
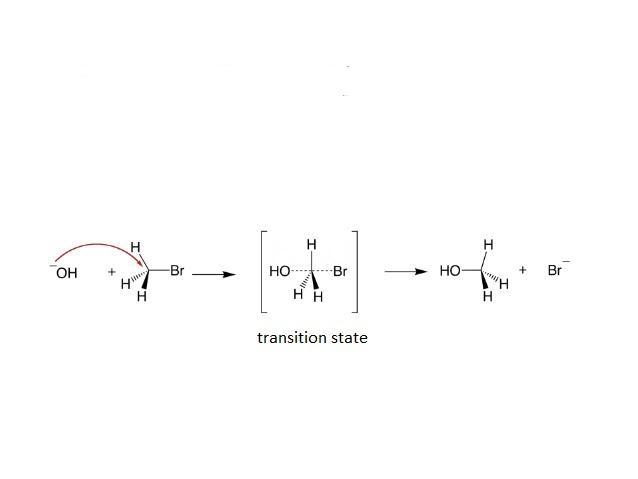
- Methyl halides are more reactive than the primary alkyl halides towards the SN2 reaction. Similarly the primary alkyl halides are more reactive towards the SN2 reaction then the secondary halides.
- This is due to the steric hindrance and the electron donating effect of the alkyl group which increases the electron density on the carbon which is attached to the halogen and makes it less electrophilic.
Note: For SN2 reaction higher will be the temperature more elimination product we get. The more elimination products we get, the substitution product will be less because the amount of the reactant is limited. This is because the activation energy for a particular reaction is higher for elimination reaction than the substitution reaction for the same reaction.
