Question
Question: Keeping the principle of conservation of momentum in mind, which of the following collision diagrams...
Keeping the principle of conservation of momentum in mind, which of the following collision diagrams may not be correct?
a)
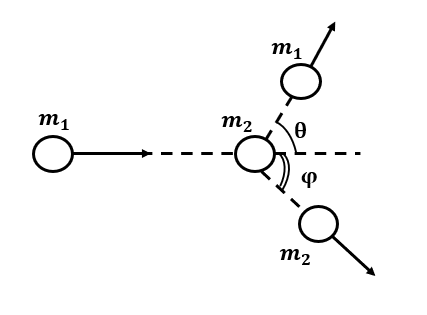
b)
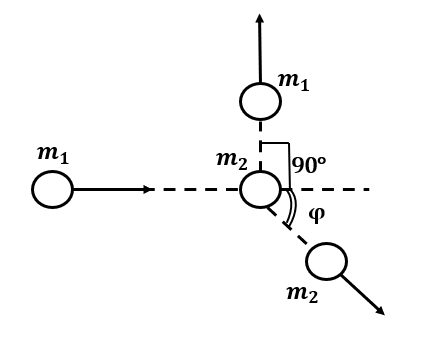
c)
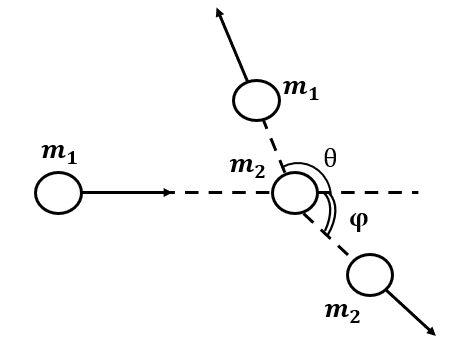
d)
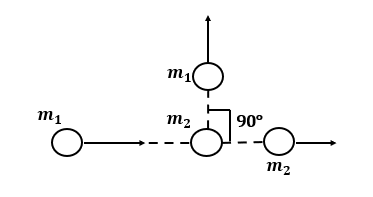
Solution
Initially, the system has the only momentum accompanying the x-axis, but the system has whole non-zero momentum accompanying the y axis after the collision. But the arrangement should have momentum along only the x-axis according to the conservation law of linear momentum.
Complete step-by-step solution:
An influential theory in science is momentum conservation law. This law defines what results in momentum when two objects hit. The law says that when two objects hit in a closed system, the whole momentum of the two objects before the crash is equal to the entire momentum of the two objects following the collision. The momentum of a specific object may vary, but the total momentum must keep the same.
When two objects collide with each other, this is termed a collision. In science, a collision does not have to include an accident but can be any situation where two or more traveling objects apply forces on each other for a short period.
Momentum is an estimation of mass in motion. Any object that is traveling has momentum. The momentum of an object is the mass times the velocity.
Conservation of momentum is a significant law of physics that states that the momentum of a system is fixed if no outer forces are operating on the system. Linear momentum conservation is based on Newton's second law of motion, stating that the total momentum persists in a separate system.
At the start, the momentum is along the x-axis, but after the collision, there is non-zero momentum in the y-direction, but the system should have momentum in the x-direction only. So, Option (d) does not obey the conservation of linear momentum.
Therefore, Option (d) is correct.
Note: If there is zero external force performing on the system, the momentum is fixed. When two objects are hit in an isolated system, the complete momentum of the two objects before the collision leads to the total momentum of the two objects following the collision. Momentum is always preserved in any collision, whether the collision is an elastic or a non-elastic collision; Nevertheless, kinetic energy is not fixed in a non-elastic collision; the kinetic energy is transformed into potential energy, or heat energy, etc.
