Question
Question: IUPAC name of \(N{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH\)? A.4-aminobutanoic acid B.1-amino-4-b...
IUPAC name of NH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−COOH?
A.4-aminobutanoic acid
B.1-amino-4-butanoic acid
C.4-amino-2-butenoic acid
D.1-amino-2-butenoic acid
Solution
Identify the parent hydrocarbon and the functional groups attached to it. Since it is a polyfunctional compound, the suffixes and prefixes should be given according to the order of preference. The order of decreasing priority for some functional group is: −COOH,−SO3H,−COOR,−COCl,−CONH2,−CN,−HCO,−CO,−OH,−NH2.
Complete step by step answer:
Organic chemistry deals with millions of compounds. To identify them, a systematic method of naming has been developed known as IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system of nomenclature.
According to this system of nomenclature, the names are correlated with the structure such that the reader or listener can deduce the structure from the name.
A systematic name of an organic compound is generally derived by identifying the parent hydrocarbon and the functional group(s) attached to it.
By further using prefixes and suffixes, the parent name can be modified to obtain the actual name.
A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms bonded together in a unique manner which is usually the site of chemical reactivity in an organic molecule.
The given organic compound, NH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−COOH, is a polyfunctional compound. It has two functional groups- −NH2 and −COOH.
One of the functional groups is chosen as the principal functional group and the compound is then named on that basis. The remaining functional group is called the subordinate functional group and is named as substituents using the appropriate prefix.
The choice of principal functional group is made on the basis of the order of preference. The order of decreasing priority for some functional groups is:
−COOH,−SO3H,−COOR,−COCl,−CONH2,−CN,−HCO,−CO,−OH,−NH2
Hence, −COOH is the principal functional group and −NH2 is the substituent.
The prefix for −NH2 is ‘amino-’ and the suffix for −COOH is ‘-oic acid’.
Now we need to find the parent chain containing the principal functional group.
The numbering should be such that the principal functional group gets the lowest number. The parent chain contains 4 carbon atoms including the C atom of −COOH. Hence the parent hydrocarbon is butane. Now we need to add the appropriate suffix and prefix. The substituent −NH2 is on C-4.
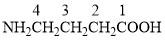
Hence, the answer is (A) 4-aminobutanoic acid.
Note: While counting the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain we must count the carbon atom in the principal functional group.
If there are more than one functional group of the same type, their number is indicated by adding di, tri, etc. before the class suffix.
