Question
Question: IUPAC name of is: 
A. Formyl ethanoic acid
B. 2-formyl propanoic acid
C. 2-carboxy propanal
D. 2-methyl propane
Solution
We need to talk about the IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds. IUPAC is a universally recognized system for chemical nomenclature and terminology.It gives us a uniform and consistent nomenclature and terminology for organic compounds. This convenience is required because there are a number of organic compounds identified and each must have a systemic nomenclature which is given by the IUPAC system. The system names compounds on the basis of the number of carbon atoms, presence of functional groups, type of bonding between carbon atoms and on various other factors.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to remember that the basic set of rules to be followed while naming any compound under the IUPAC system are as follows:
1. Predict whether the given compound is saturated or unsaturated: Saturation and unsaturation depends on the type of bonding between carbons. Saturated compounds contain carbons connected by single bonds only and unsaturated compounds contain double or triple bonds. Alkanes being the roots for naming organic compounds are a family of saturated hydrocarbons and hence they have the suffix “-ane”. In case of unsaturated hydrocarbons, the suffix “-ene” is used for compounds having double bonds and “-yne” for triple bonds.
2. Locate the longest continuous carbon chain which is the parent chain: Depending on the number of carbons in the parent chain, the alkanes are names as methane (one carbon parent chain), ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, heptane, octane, nonane, decane (ten carbon parent chain).
3. Locate the functional groups: The functional groups are carboxylic acid (-COOH), aldehyde (-CHO), ketone (-CO), alcohol (-OH) and amine (−NH2).The prefix and suffix in the nomenclature of an organic compound containing these functional groups are given in the table below.They are listed on the basis of their priority. If an organic compound contains more than one functional group, then the group listed on the top of the table receives higher priority.
| Functional group | Prefix | Suffix |
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acid | Carboxy- | -oic acid (-carboxylic acid) |
| Aldehyde | Oxo-(formyl) | -al (carbaldehyde) |
| Ketone | Oxo- | -one |
| Alcohol | Hydroxy- | -ol |
| Amine | Amino- | -amine |
4. Locate the substituents: Substituents such as methyl (−CH3), ethyl (−CH2CH3),etc present in the compound replace “ane” ending of alkane with “yl”.
5. Number the chain: This is the most important step to name branched compounds as well as those which have substituents or more than one functional group.The parent chain should be numbered in the direction such that the position number of the first substituent is the smaller number. If the first substituents from either end have the same number, then number so that the second substituent has the smaller number.
Let us now name the given compound
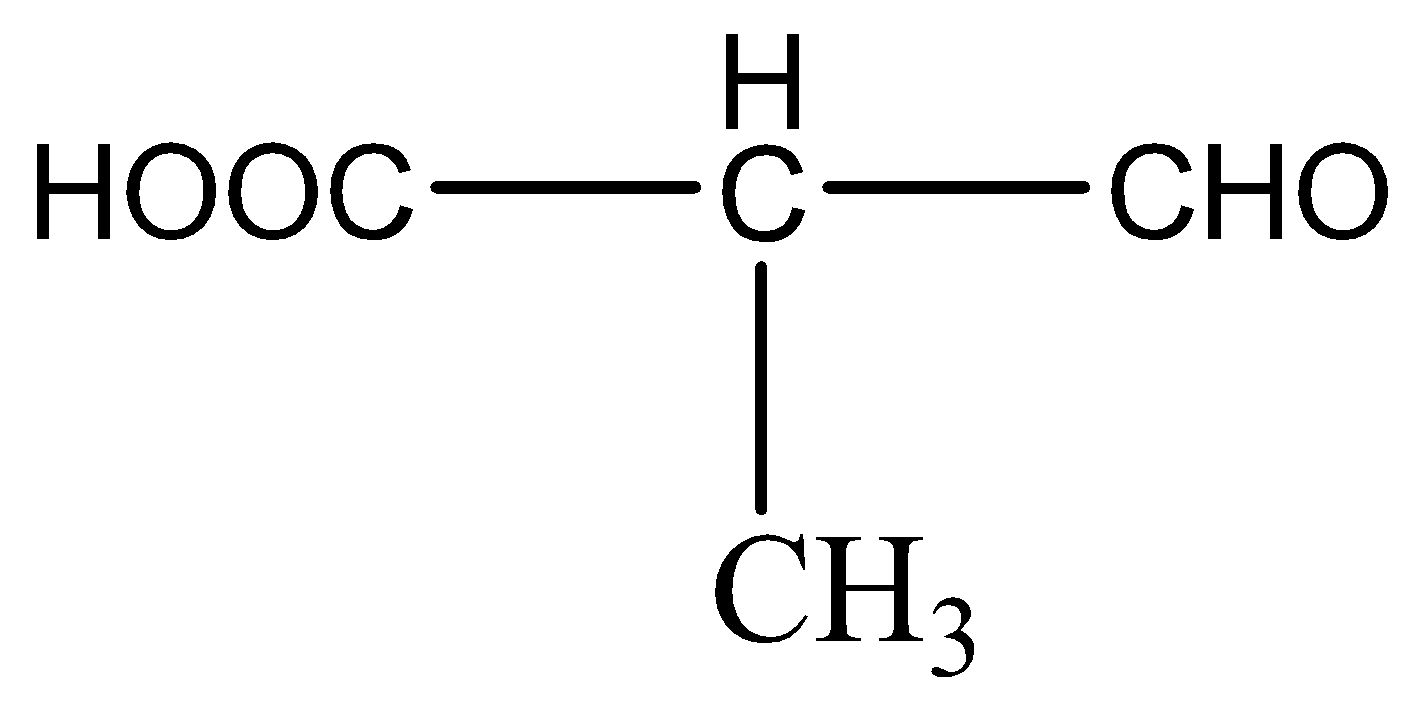
This compound is a saturated hydrocarbon, the parent chain consists of three carbons and has two functional groups- carboxylic acid (-COOH) and aldehyde (-CHO). Since -COOH has a higher priority over -CHO, the -COOH group is the primary functional group and numbered as 1. Hence the IUPAC name is 2-formyl propanoic acid.
Hence,the correct option is option (B).
Note:
We must be noted that the rules for naming organic compounds is a complex and long data depending on the type of organic compound to be named. In case of a molecule such as the given
2-formyl propanoic acid, numbering the parent chain correctly is the most important step. Numbering specifies the position of the functional groups or any substituent present.
