Question
Question: Isopropyl chloride + A \[\xrightarrow{\Delta }\]2-ethoxy propane + NaCl. The compound (A) is: (A.)...
Isopropyl chloride + A Δ2-ethoxy propane + NaCl. The compound (A) is:
(A.) C2H5Cl
(B.) C2H5ONa
(C.) CH2N2
(D.) CH3ONa
Solution
Williamson synthesis is the most commonly used method to prepare ethers from alkyl halides. It is a SN2 reaction in which a metal alkoxide reacts with alkyl halide and forms ether. The alkoxide reagent used in this reaction can be prepared by the reaction of a strong base with alcohol. Williamson synthesis is suitable for the preparation of various unsymmetrical ethers.
Complete step by step answer:
The given reaction is as follows.
Isopropyl chloride + A Δ2-ethoxy propane + NaCl.
To know about the compound A, we should know the structures of the isopropyl chloride and 2-ethoxypropane.
The structure of isopropyl chloride and 2-ethoxypropane as follows.
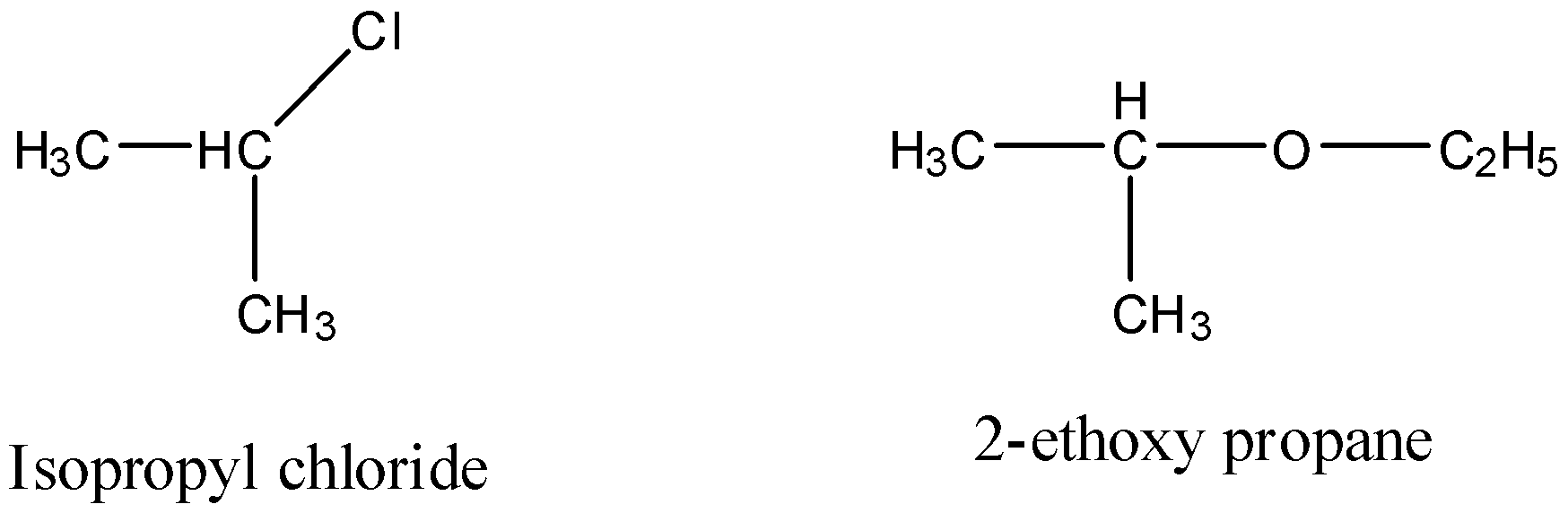
From the above structures we can easily identify the alkoxide used in the given reaction.
The total reaction we can write as follows based on the structures of the isopropyl chloride and 2-ethoxypropane.
In the above reaction isopropyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide and forms 2-ethoxy propane and sodium chloride.
Therefore the alkoxide involved in the above reaction is sodium ethoxide. Here, the compound A = sodium ethoxide.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: SN2means bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In SN2reaction there is an involvement of both the reactants, and then only it is called bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In SN2reaction there is an inversion in the structure of the product. Then this SN2reaction is called Walden inversion reaction. 2-ethoxy propane is unsymmetrical ether.
