Question
Question: Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms: a) Ethylene b) Acetone c) Ether d) Acetaldehyde...
Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms:
a) Ethylene
b) Acetone
c) Ether
d) Acetaldehyde
Solution
Iso group can be defined as the structural isomer of a straight chain alkane where the second carbon will be attached to a methyl group. When any functional group is attached to the second carbon, the hydrocarbon will be called as a secondary carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
Alcohols are the functional group where the hydrocarbon is attached to the −OH group. The hydrocarbons can include alkanes, alkenes, aromatic compounds, etc.
When we oxidise the alcohols we get an aldehyde or a ketone depending on the type of carbon where the alcoholic group is attached.
A Primary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to only one carbon. For example, \Propan−1−ol that can be represented as
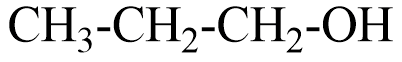
A secondary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to two carbons in the structure. For example, Butan−2−ol that can be represented as
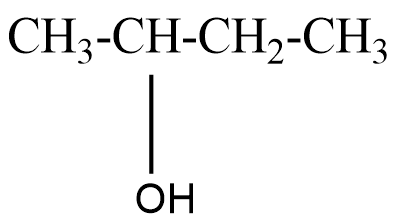
A tertiary alcohol will be said to the compound where the alcoholic group is attached to the carbon which is attached to three carbons in the structure. For example, 2−Methylpropan−2−ol that can be represented as
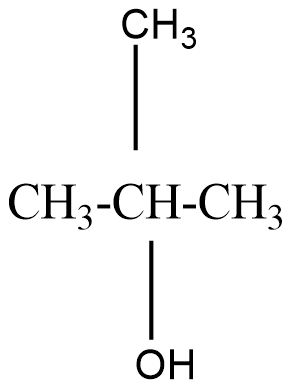
On oxidation of primary alcohol we get an aldehyde. But on oxidising a secondary alcohol, a ketone is usually formed.
The structure of isopropyl alcohol can be represented as-
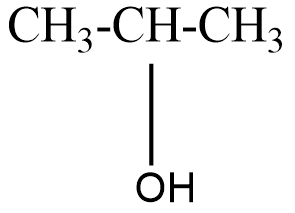
On oxidation of isopropyl alcohol, a secondary alcohol we get a ketone namely, acetone.
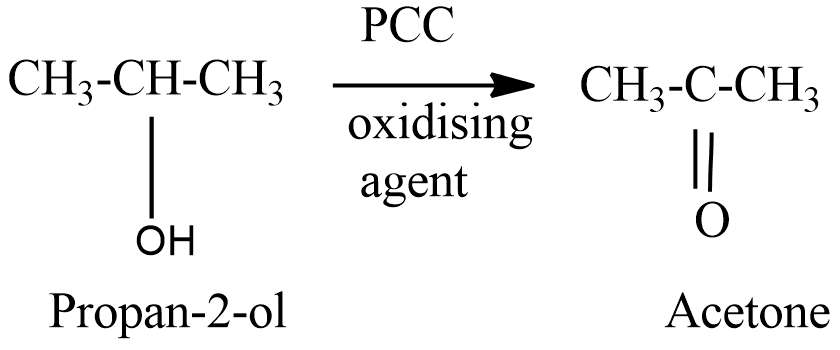
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
There are different oxidising agents that can be used to oxidise particularly aldehyde and ketones, for example CrO3 , PCC. PCC is used particularly to oxidise alcohol into ketone. On oxidising a carbonyl compound (aldehyde and ketone) the formation of carboxylic acid can be seen.
