Question
Question: Isobutyl chloride \(\xrightarrow [KOH] {alc.}X\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{{{H}_{2}}O}Y\) What is IUPA...
Isobutyl chloride alc.KOHXH2OH+Y
What is IUPAC name for Y?
A. isobutyl 1 alcohol
B. tert butyl alcohol
C. 2-methylpropan-2-ol
D. 2-methylpropan-1-ol
Solution
Alcoholic KOH is a dehydrohalogenation agent. Dehydrohalogenation refers to the removal of hydrogen halides present in the compounds. To find X and Y, we first need the structure of isobutyl chloride.
Complete step by step solution:
-Isobutyl chloride is a tertiary carbon compound with a chloride group. This chloride group can be removed easily by dehydrohalogenation. The resulting compound forms alkene.
-When an alkene undergoes hydrolysis, alcohol formation takes place due to the high electronegativity of an alkene compared to alkane. So our final product will be alcohol.
-To name the structures, we first need to draw the reactant structure correctly else the compound formed will be different and so will the name. The structure of isobutyl chloride can be shown as
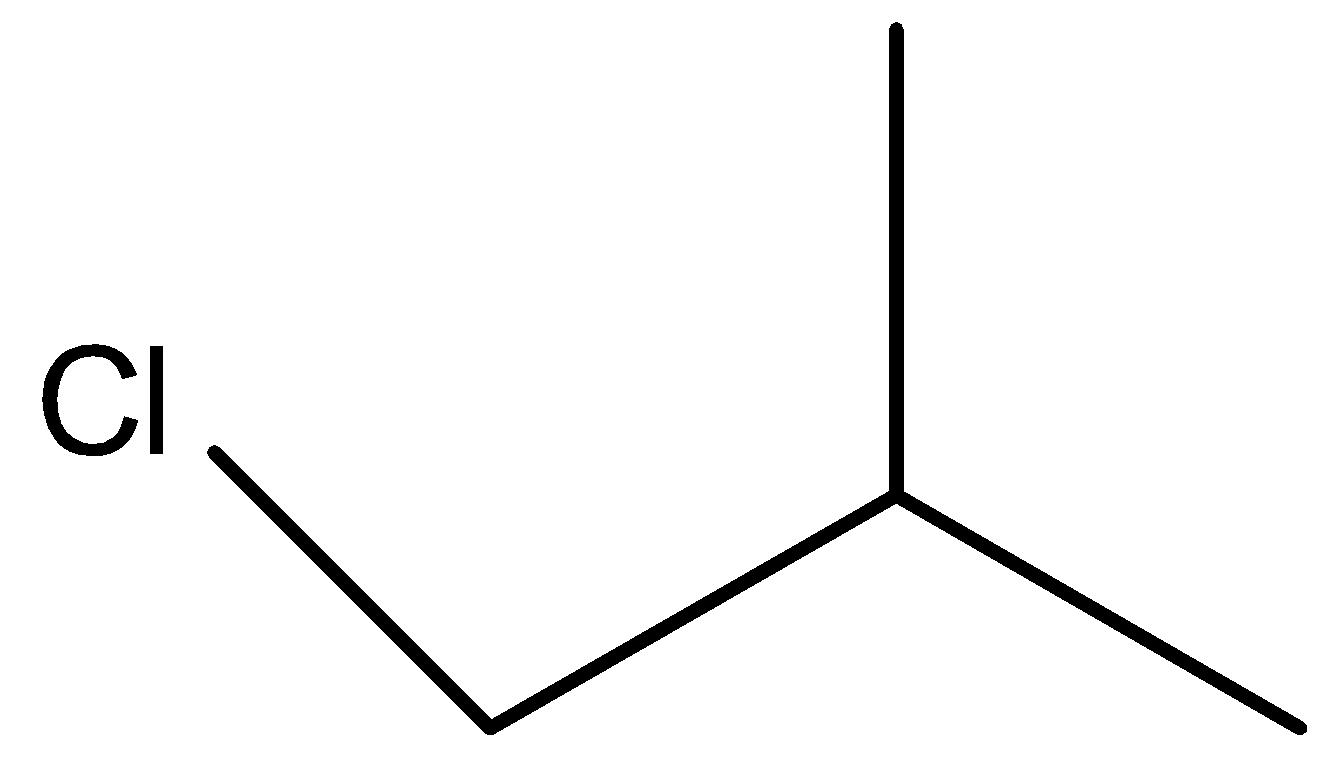
- Hydrogen and chlorine will get removed from opposite directions to form an alkene and this process is dehydrohalogenation. This leads to the formation of compound X that can be shown as
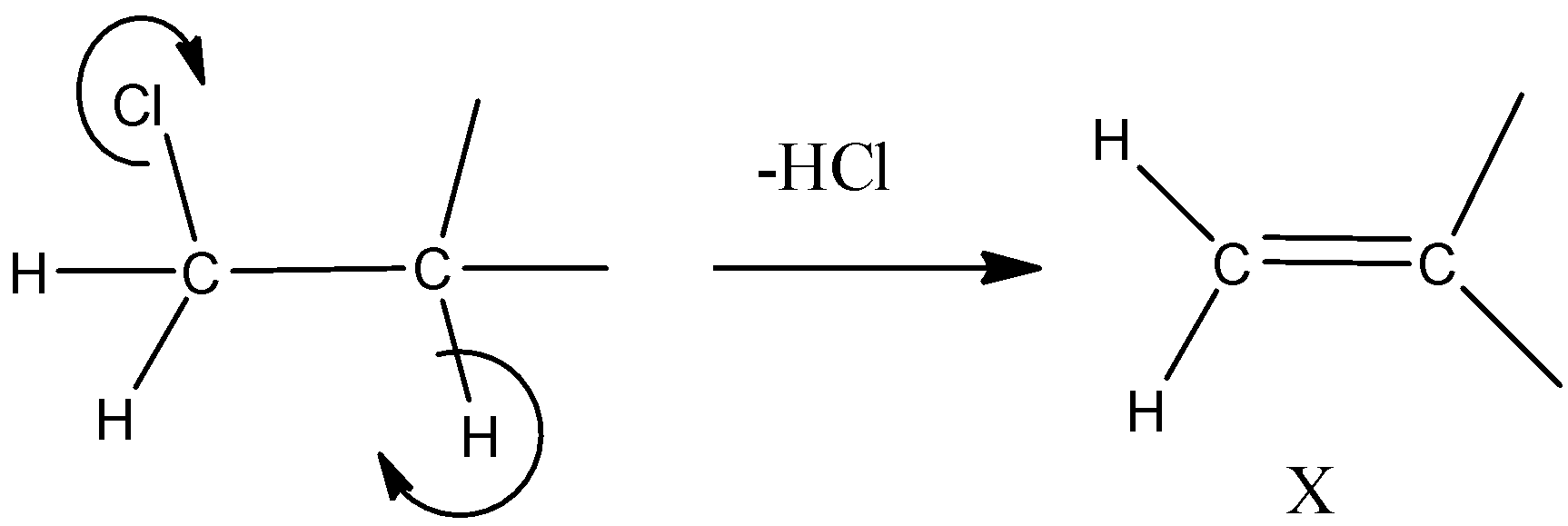
-The IUPAC name of compound X can be written as 2-methylpropene as it has a methyl group in the second carbon atom. Now this compound undergoes hydrolysis forming alcohol by the protonation of alkene and the reaction can be shown as
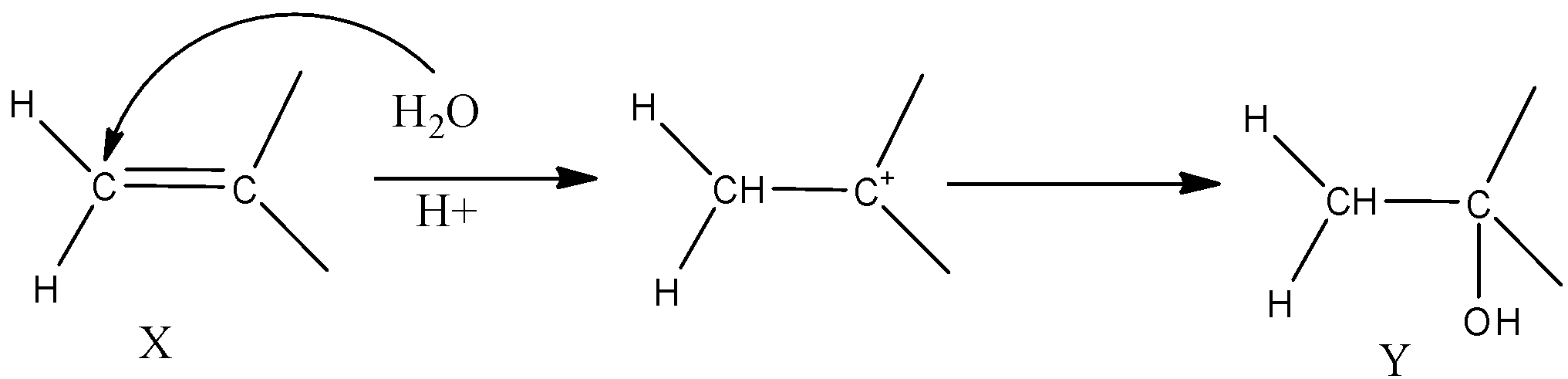
-Now we need to find the IUPAC name of the compound Y. Numbering the groups I the compound, we get the locant position as
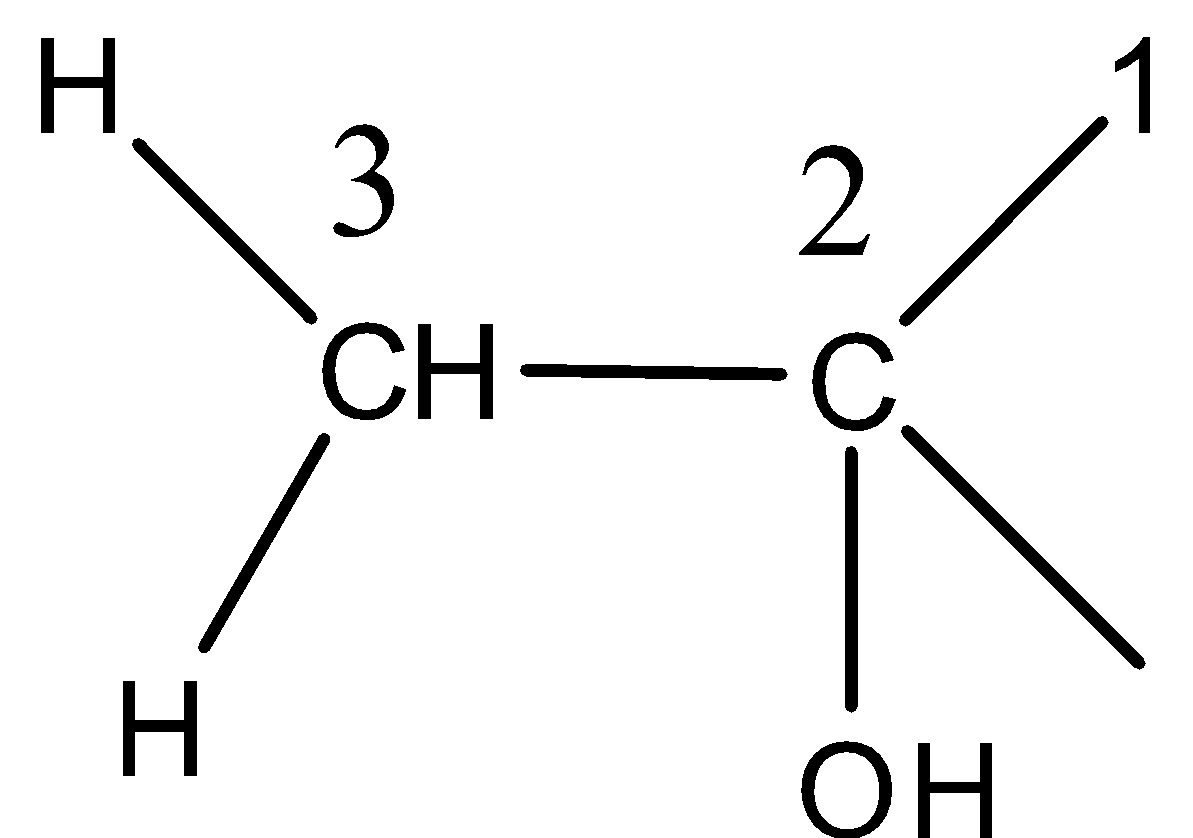
Therefore the name for this compound Y is 2-methylpropan-2-ol and the correct option is C.
Note: The intermediate formed during the reaction from X to Y is a carbocation which can rearrange itself to gain the stability. This is why the addition of the –OH group does not occur at the position 1 locant.
