Question
Question: Is there some link between the size of an animal's ears and their hearing?...
Is there some link between the size of an animal's ears and their hearing?
Solution
The human hear-able framework permits us to see and confine sounds in our physical climate. The human feeling of hearing is credited to the heart-able framework, which utilizes the ear to gather, enhance, and transduce sound waves into electrical driving forces that permit the cerebrum to see and confine sounds.
Complete step by step answer:
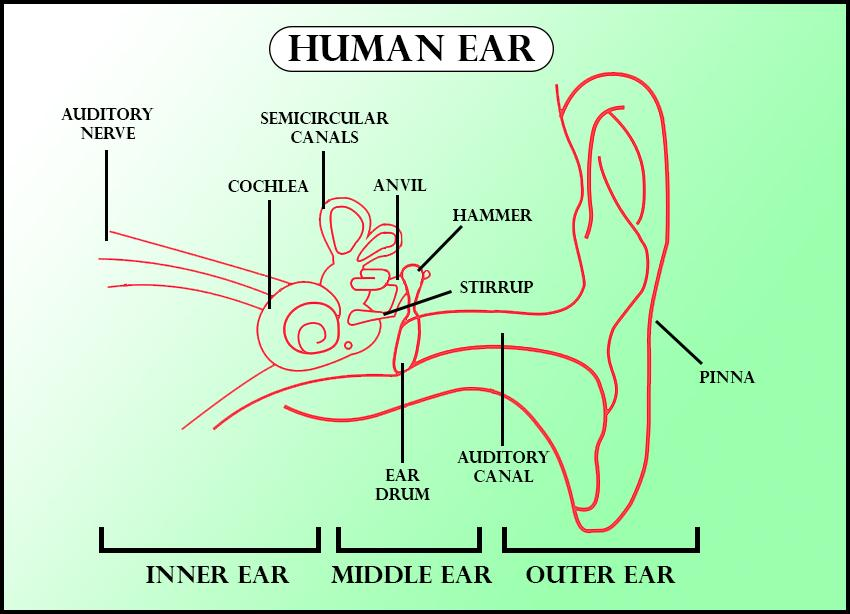
The ear is the fundamental tangible organ of the heart-able framework. It plays out the principal handling of sound and houses the entirety of the tangible receptors required for hearing. The ear's three divisions (external, center, and inward) have particular capacities that join to permit us to hear.
The human hear-able framework permits the body to gather and decipher sound waves into important messages. The principle tactile organ liable for the capacity to hear is the ear, which can be separated into the external ear, center ear, and internal ear. The inward ear contains the receptor cells vital for both hearing and harmony upkeep. People additionally have the uncommon capacity of having the option to gauge where sounds begin from, regularly called sound restriction.
The cycle of hearing:
- Hearing starts with pressure waves hitting the heart-able trench and closures when the mind sees sounds. Sound gathering happens at the ears, where the pinna gathers, reflects, weakens, or enhances sound waves.
- These waves travel along the hear-able channel until they arrive at the eardrum, which vibrates in light of the adjustment in pressure brought about by the waves. The vibrations of the eardrum cause motions in the three bones in the center ear, the remainder of which sets the liquid in the cochlea moving.
- The cochlea isolates sounds as per their place in the recurrence range. Hair cells in the cochlea play out the transduction of these sound waves into afferent electrical motivations.
- Auditory nerve filaments associated with the hair cells structure the winding ganglion, which communicates the electrical signs along the hear-able nerve and inevitably on to the cerebrum stem. The mind reacts to these different frequencies and makes a total sound from them.
Note: People can hear a wide assortment of sound frequencies, from around 20 to 20,000 Hz. Our capacity to pass judgment or gauge where a sound starts, called sound restriction, is subject to the conference capacity of every ear and the specific nature of the sound. Since every ear lies on the opposite side of the head, a sound arrives at the nearest ear first, and the sound's sufficiency will be bigger (and along these lines stronger) in that ear.
