Question
Question: Is \({\text{V}}\) the reference vector for parallel \({\text{RC}}\) circuits?...
Is V the reference vector for parallel RC circuits?
Solution
Try to obtain a circuit diagram in your mind containing Resistance R and Capacitance C and analyse voltage across resistance and capacitor. You will find that the voltage across the resistance and capacitor is the same.
Complete step by step solution:
As the voltage across the resistance and capacitor is the same.
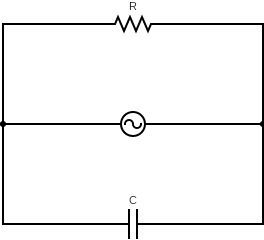
This is so because voltage is connected in parallel with resistance and the capacitor. The current through the individual elements the resistance and the capacitor differs. Through these elements there is also a phase difference of 2π.
Since the voltage is the common factor, the vector diagram will have 2currents relative to the voltage reference vector.
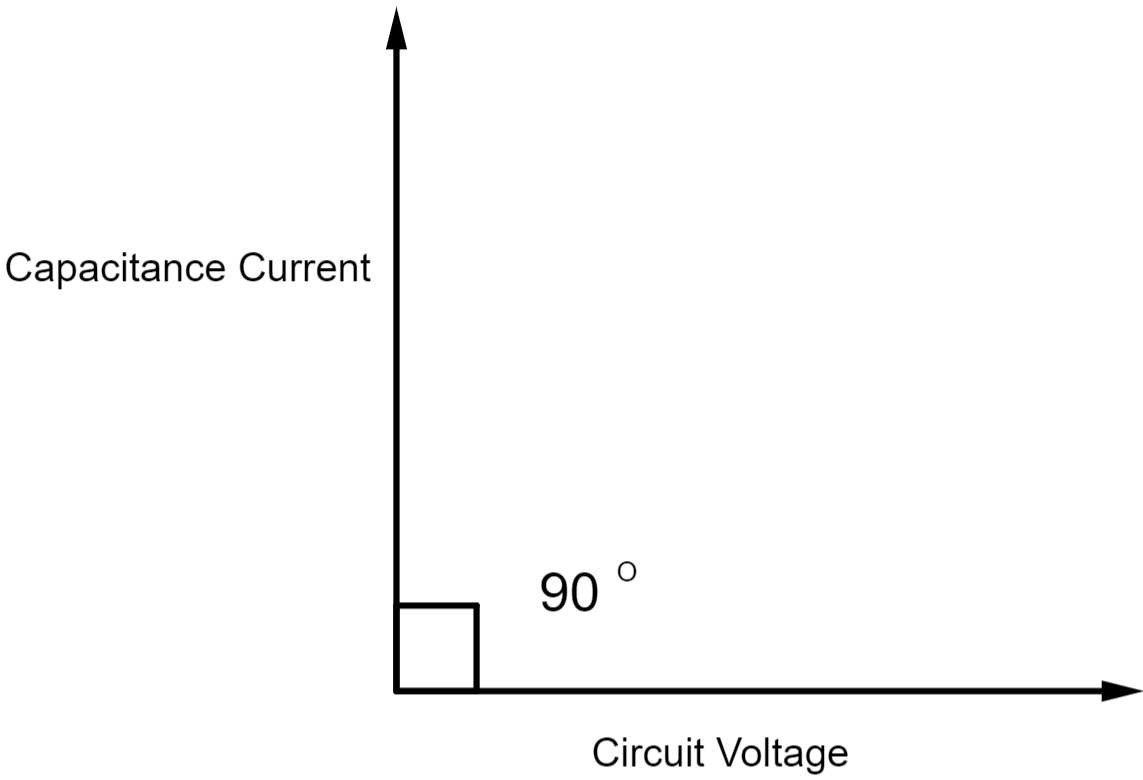
We can make phase diagrams to observe this phase difference between the current of the two elements.
Note:
The parallel RLC circuit is the exact opposite to the series circuit of LCR. The analysis of parallel RLC circuits can be more mathematically difficult than series RLC circuits. Instead of current being common to all so we need to find the individual branch currents through each element. Common between the three is voltage in this case.
