Question
Question: Is skin color an example of incomplete dominance in humans?...
Is skin color an example of incomplete dominance in humans?
Solution
Dwarf, tall, and pink are all phenotypic or morphological characteristics, as we all know. The experiment Portrayed by Gregor Mendel, in his studies of the genetics of the pea plant. Each being carries two copies of trait- one was dominant trait and one is recessive. Heterozygous tall plant with pink flower is test crossed with homozygous recessive as a result different phenotypes are produced in the F1 offspring.
Complete answer:
By performing a test cross, it can be determined that the individual is homozygous or heterozygous dominant. In a test cross, an individual bred with another individual that is homozygous for the recessive trait and offspring of the test cross is determined. The test has two possibilities- if any offspring produced expresses the recessive trait, the individual is heterozygous. If all the offspring produced express a dominant trait, the individual is homozygous for the dominant allele.
Test crosses have a variety of applications like- model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans and drosophila melanogaster. There are also limitations in test cross- It can be time-consuming for some experiments as organisms require long time for growth and generation. A large number of offspring require reliable data due to statistics. Test crosses are only useful when complete dominance is there. Incomplete dominance does not show test cross.
Note:
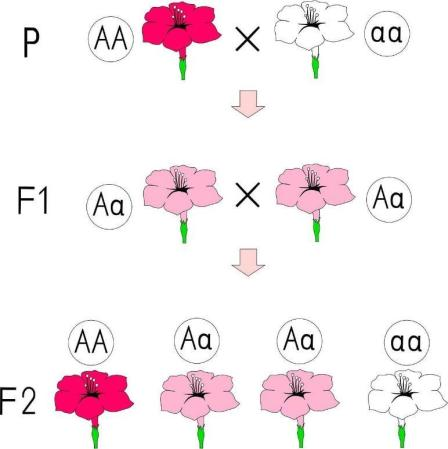
Skin color is shown by the amount of melanin pigment in the body. The amount of pigment is demonstrated by certain genes. Hence, skin color is an example of incomplete dominance as it is maintained by multiple genes. And also, they show polygenic inheritance. Another example of incomplete dominance is mirabilis Jalapa also known as 4o’ clock plant which bears flowers of white and pink pigment color when red and white flowers are crossbred together.
