Question
Question: Is n-butane and isobutane an example of two isomers of butane?...
Is n-butane and isobutane an example of two isomers of butane?
Solution
Isomers in chemistry are molecules or polyatomic ions that have the same molecular formula — that is, the same number of atoms of each element — but different atomic configurations in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or potential of isomers. Isomers don't always have the same chemical or physical characteristics as one another. Structural or constitutional isomerism, in which the bonds between the atoms differ, and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the relative locations of the atoms differ, are the two primary types of isomerism.
Complete answer:
A structural isomer of a chemical is a compound with the same number of atoms of each element as the original, but logically different bonds between them. Previously, the word "metamer" was used to describe the same idea. A skeletal isomer of a chemical is a structural isomer that varies from it in terms of the atoms and bonds that make up the molecule's "skeleton." For organic molecules like alkanes, this generally refers to the carbon atoms and their bonds.
The −CH2 unit distinguishes members of the homologous sequence of alkanes from one another. The molecular mass grows as the number of carbon atoms in the series increases. Butane is made up of four carbon atoms. As a result, these four carbon atoms can organise themselves in two distinct ways. They can form a chain of four carbon atoms in a straight line or a chain of three carbon atoms with one side chain. Butane is a four-carbon alkane with the chemical formula C4H10 . There are two isomers of butane: n-butane and isobutane.
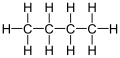
n-Butane is a single-covalently bonded straight-chain molecule having four carbon atoms.
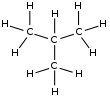
Isobutane or 2-methylpropane is another isomer in which three carbon atoms from the parent chain are substituted for one carbon atom in the side chain at C-2 of the parent chain. All carbon atoms have four valencies, which are filled by carbon or hydrogen atoms.
Butane's chemical formula is C4H10 . With this molecular formula, there are two potential isomers. The first is n-butane, which is composed of all four carbon atoms in the parent chain and has the structural formula CH3−CH2−CH2−CH3 .
Isobutane, which has three carbon atoms in the parent chain and one in the side chain as a methyl group, is another isomer.
Hence yes is the answer.
Note:
Conformational isomerism is a kind of stereoisomerism in chemistry in which isomers can be interconverted simply by rotating around formally single bonds. While any two atomic configurations in a molecule that differ by rotation around single bonds are considered distinct conformations, conformations that correspond to local minima on the potential energy surface are called conformational isomers or conformers.
