Question
Question: Is EDTA an Acid or Base?...
Is EDTA an Acid or Base?
Solution
EDTA stands for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. It is widely used in complexometric titrations and is a well-known metal-chelating agent, extensively used for the treatment of heavy metal poisoning. EDTA has four groups of carboxyl and two groups of amines.
The structure of EDTA is given below-
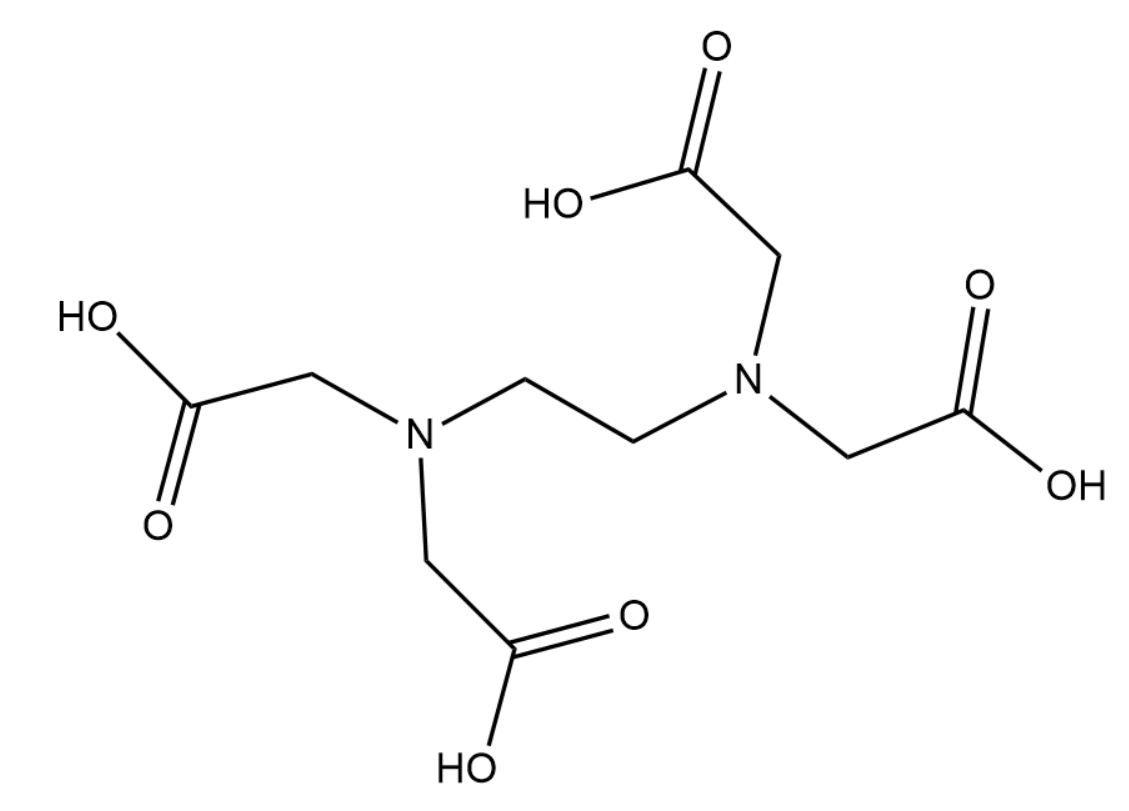
Complete answer:
From the name itself it is clear that EDTA is a weak acid. It behaves as an amino polyprotic acid. Due to the presence of the four carbonyl groups it can lose that hydrogen thus gaining a negatively charged COO− group in each of the four acid groups. Thus EDTA is mildly acidic in nature.
EDTA can lose all 4 of its hydrogen and formEDTA4−. This along with the lone pairs on each nitrogen can form a total of 6 bonds with the metal ion. This is the reason why EDTA is called a hexadentate ligand. The metal-EDTA complex usually has an octahedral geometry.
Note:
Complexometric titration is a form of volumetric analysis that is used mainly to determine metal ions by use of complex-forming reactions. When EDTA is used alongside Eriochrome Black T (a blue indicator) the colour of the solution changes from wine red to blue indicating the presence of metal ions such asCa2+,Mg2+. EDTA has a claw-like structure that we use to stick and grab other molecules and thus forms coordination complexes with them.
