Question
Question: Is 2-methyl pentane optically active?...
Is 2-methyl pentane optically active?
Solution
We need to know that the compound that is capable of rotating the plane of polarized light i.e. it is capable of rotation is known as an optically active compound. All chiral molecules are optically active. Example: R-Lactic Acid is chiral and thus is optically active i.e., can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Complete answer:
We have to know that the compounds which are capable of rotating the polarized light are said to be optically active molecules. It should have a chiral center. A chiral Carbon is an asymmetric carbon with four different groups, and also forms non superimposable mirror images.
The structure of 2-methyl pentane can be given as:
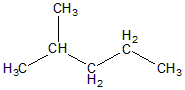
Here as we can see C2 carbon has one H two methyl groups and one CH2−CH2−CH3 group. Hence carbon C2 is not chiral as the four groups attached are not different.
C1 has 3 hydrogen and one −CH(CH3)−CH2−CH2−CH3 groups attached. It's also optically inactive
C3 has two hydrogens attached and one CH3−CH(CH3) and −CH2−CH3 group . Hence, it’ll be optically inactive.
C4 has two hydrogens attached and one −CH3 and −CH2−CH(CH3)−CH3 . Hence it would also be optically inactive.
C5 has three hydrogens and 1 CH3−CH(CH3)−CH2−CH2 attached hence it’ll be also optically inactive
Since there are no asymmetrical carbons present, the molecule is achiral and hence will not exhibit optical activity.
Hence 2-methyl pentane is Optically Inactive.
Note:
We need to remember that if a molecule has non-super imposable mirror images, then they are said to be enantiomers. Enantiomers are basically the mirror images of a compound. Enantiomers are always chiral and optically active. Example: D-Glucose and L-Glucose are enantiomers of each other.
