Question
Question: Intervertebral disc occurs in (a) Wall of Heart (b) Wall of Liver (c) Pubic Symphysis (d) I...
Intervertebral disc occurs in
(a) Wall of Heart
(b) Wall of Liver
(c) Pubic Symphysis
(d) In between two Vertebrae
Solution
The intervertebral discs (or discs) are fibrocartilages lying between adjacent surfaces of the spine. Each disc is able to absorb the stress and the shock of the body that occurs during movement and it prevents the vertebrae from grinding against one another.
Complete step by step answer:
In humans, the vertebral column is formed by the serial arrangement of twenty-six units called vertebrae and is dorsally placed. The intra articular disc is a thin, oval plate form of fibrous cartilage. Each interarticular disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), which will allow the slight movement of the vertebrae, and it acts as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together. Hence Inter-articular disc occurs in between the 2 vertebrae. It is a cushion of fibrocartilage and also the principal joint between two vertebrae within the vertebral column. There are 23 discs within the human spine: 6 within the cervical region (neck), 12 within the thoracic region (middle back), and 5 within the lumbar region (lower back).
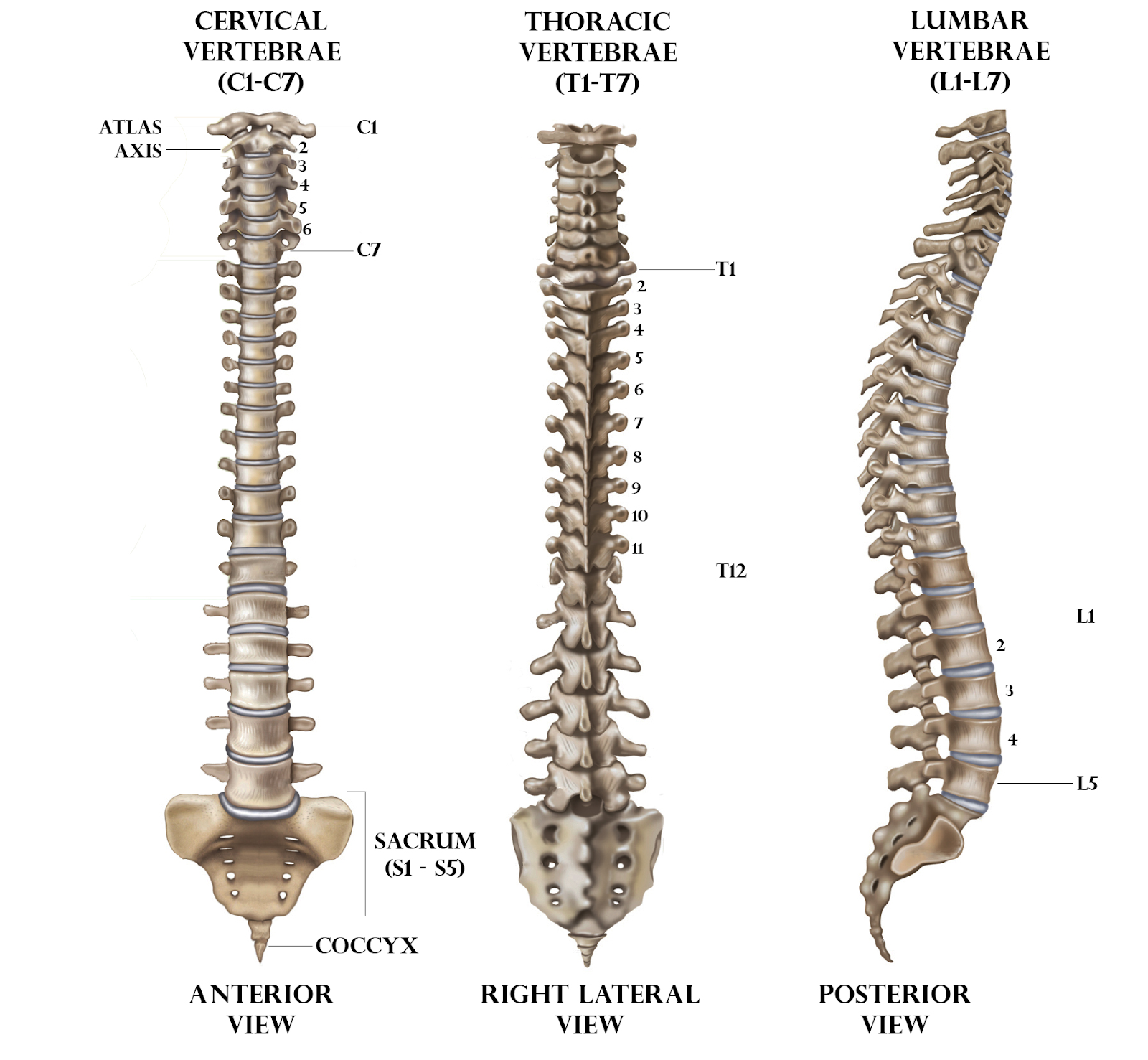
So, the correct answer is 'In between two vertebrae'.
Additional Information: The intervertebral discs are fibrocartilaginous which lies between adjacent surfaces of the vertebrae. Intervertebral discs, like other cartilages, haven't any blood supply. Intervertebral discs are innervated through various nerve fibers. There are 23 intervertebral discs present in the spine: Six within the cervical region (neck), twelve within the thoracic region (middle back), and five within the lumbar region (lower back). The intervertebral discs are approximately seven to 10 mm thick and 4 centimeters in diameter (Anterior-Posterior Plane) within the lumbar region of the spine.
Note:
- The human spinal column consists of about thirty-three vertebrae interconnected by fibrocartilaginous intervertebral discs. There is no intervertebral disc in between the first cervical bone and the second cervical bone.
- Disc thickness has a general order in which it increases from cervical to thoracic to lumbar. The thickness of the discs relative to the dimensions of vertebral bodies is greater for the cervical and lumbar region. This shows us the increased range of motion found in those regions.
