Question
Question: Indicate the \(\sigma\) and \(\pi\) bonds in the following molecules. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\...
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules.
C6H6, C6H12, CH2Cl2, CH2=C=CH2, CH3NO2, HCONHCH3
Solution
The single bonds in a compound are known as the σ bonds. If there are double bonds in a compound then one bond is σ bond and one is the π bond. If there are triple bonds in a compound then one bond is the σ bond and two are the π bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the molecule has covalent bonds there are sigma bonds and pi bonds. The sigma bonds are represented by σ and the pi bonds are represented by π.
The bond formed between two atoms by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals along the intermolecular axis is known as the sigma bond.
The bond formed by the lateral overlap of the atomic orbitals at right angles to the intermolecular axis is known as the pi bond.
1. Consider the compound C6H6:
The structure of C6H6 is as follows:
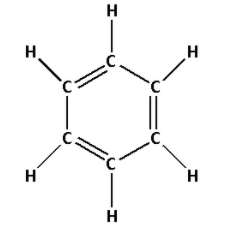
- The structure of C6H6 contains three single bonds and three double bonds.
- Three single bonds indicate that there are three σ bonds. And three double bonds indicate that there are three σ bonds and three π bonds. Thus, there are six σ bonds and three π bonds.
- Thus, C6H6 has six σ bonds and three π bonds.
2. Consider the compound C6H12:
The structure of C6H12 is as follows:
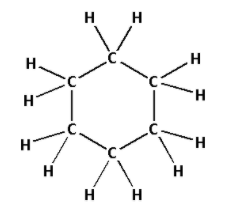
- The structure of C6H12 contains eighteen single bonds.
- Eighteen single bonds indicate that there are eighteen σ bonds. Thus, there are eighteen σ bonds and zero π bonds.
- Thus, C6H12 has eighteen σ bonds and zero π bonds.
3. Consider the compound CH2Cl2:
The structure of CH2Cl2 is as follows:
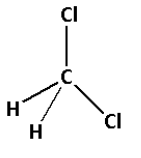
- The structure of CH2Cl2 contains four single bonds.
- Four single bonds indicate that there are four σ bonds. Thus, there are four σ bonds and zero π bonds.
- Thus, CH2Cl2 has four σ bonds and zero π bonds.
4. Consider the compound CH2=C=CH2:
The structure of CH2=C=CH2 is as follows:
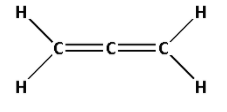
- The structure of CH2=C=CH2 contains four single bonds and two double bonds.
- Four single bonds indicate that there are four σ bonds. And two double bonds indicate that there are two σ bonds and two π bonds. Thus, there are six σ bonds and two π bonds.
- Thus, CH2=C=CH2 has six σ bonds and two π bonds.
5. Consider the compound CH3NO2:
The structure of CH3NO2 is as follows:
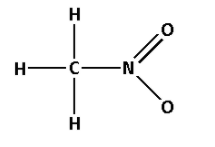
- The structure of CH3NO2 contains five single bonds and one double bond.
- Five single bonds indicate that there are five σ bonds. And one double bond indicates that there is one σ bond and one π bond. Thus, there are six σ bonds and one π bond.
- Thus, CH3NO2 has six σ bonds and one π bonds.
6. Consider the compound HCONHCH3:
The structure of HCONHCH3 is as follows:
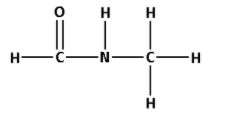
- The structure of HCONHCH3 contains seven single bonds and one double bond.
- Seven single bonds indicate that there are seven σ bonds. And one double bond indicates that there is one σ bond and one π bond. Thus, there are six σ bonds and one π bond.
- Thus, HCONHCH3 has eight σ bonds and one π bonds.
Note:
The sigma bond overlapping is very large and thus, the sigma bond is stronger. The overlapping of pi bonds is weak and thus, pi bond is weaker. The sigma bond has one-electron cloud and the pi bond has a two-electron cloud.
