Question
Question: Indicate the alkyl halides one of the following which can undergo \[S{{N}^{1}}\] reaction. a. !...
Indicate the alkyl halides one of the following which can undergo SN1 reaction.
a. 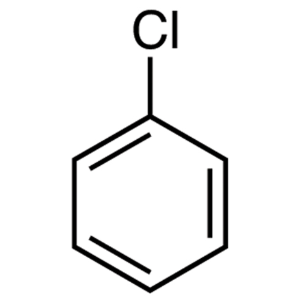
b. 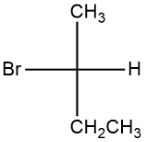
c. CH2=CHCl
d. CH2=CHCH2Cl
Solution
SN1 is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where the rate determining step is unimolecular. The reaction involves the formation of an intermediate carbocation. It is generally seen in tertiary or secondary alkyl halides with secondary or tertiary alcohols.
Complete answer:
SN1 reaction depends on the concentration of only one reactant. It occurs in two steps:
In step one the bond undergoes slow cleavage to form carbocation and in step two it completes the substitution reaction.
The order for SN1 reactions tertiary halide > secondary halide > primary halide.
Now in the given question the first compound which is chlorobenzene. Chlorine being an electron withdrawing group is still too weak to activate the ring towards substitution, and thus no reaction will occur. nucleophilic aromatic reactions generally require a very strong electron withdrawing group.
The second compound, 2-bromobutane, the halogen group here is an effective leaving group. SN2 is generally favorable for the nucleophilic substitution reaction of
2-bromobutane as it will demand more external energy for its complete reaction. Hence, it shows SN2 reaction.
The third compound, Vinyl chloride is generally unreactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction due to resonance. The lone pair of electrons on chlorine is in resonance with the C-C double bond, due to which there will be a partial double bond character in C-Cl bond.
The fourth compound, allyl chloride, mostly shows SN1 reaction as it involves the formation of intermediate carbocation. carbocation formed from allyl chloride achieves stability by resonance.
Therefore, from the above statements we can conclude allyl chloride is more reactive towards SN1 reaction,So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: SN2 is a nucleophilic substitution reaction that depends on two components. They are bimolecular with simultaneous bond-making and bond-breaking steps.
The reactivity of SN2 halides: primary> secondary> tertiary
