Question
Question: In which one of the following processes \({ C }{ O }_{ 2 }\) is not released? (A) Aerobic respirat...
In which one of the following processes CO2 is not released?
(A) Aerobic respiration in plants
(B) Aerobic respiration in animals
(C) Alcoholic fermentation
(D) Lactate fermentation
Solution
The above-mentioned process in which CO2 is not released is a metabolic process by which glucose and many other six-carbon sugars are converted into cellular energy and a specific metabolite.
Complete answer:
The processes in which CO2 is not released is the Lactate fermentation. Lactate fermentation is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that will take place in some types of bacteria and animal cells, like muscle cells. Lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and also the lactate with concomitant interconversion of the molecule NADH and NAD+.
Additional Information: Fermentation is the process of manufacturing ATP within the absence of oxygen, through glycolysis alone. As you know that glycolysis breaks a glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, producing a net gain of two ATP and two NADH molecules. Lactic acid or Carboxylic acid fermentation is the type of anaerobic respiration administered by yogurt bacteria (Lactobacillus and others) and by your own muscle cells once you work them hard and fast.
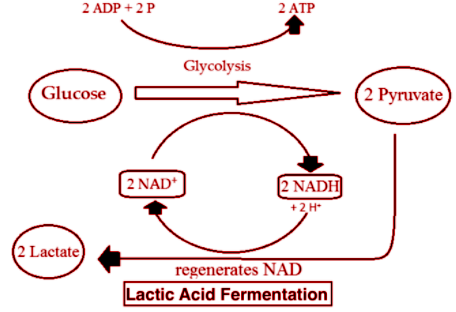
Lactic acid fermentation performs the conversion of the 3-carbon pyruvate to the 3-carbon carboxylic acid (C3H6O3) and regenerates NAD+ within the process, which helps the glycolysis to still make ATP in low-oxygen conditions. Since there's a limited supply of NAD+ available in any given cell, this electron acceptor must be regenerated to permit ATP production to continue. to realize this, NADH donates its extra electrons to the pyruvate molecules, regenerating NAD+. carboxylic acid is made by the reduction of pyruvate.
PYRUVATEC3H3O3+NADH→LACTICACIDC3H6O3+NAD+
Lactic Acid Fermentation
So, the correct answer is ‘(D) Lactate fermentation’.
Note: The very important genus of bacteria used in lactic acid fermentation is the commonly known Lactobacillus, though other bacteria and even yeast are sometimes used. Two of the foremost common applications of carboxylic acid fermentation are within the production of yogurt and sauerkraut.
