Question
Question: In which of the following reactions of alcohol there is no cleavage of \(C - O\) bond? A. Dehydrat...
In which of the following reactions of alcohol there is no cleavage of C−O bond?
A. Dehydration reaction of alcohol
B. Oxidation reaction of alcohol
C. Reduction reaction of alcohol
D. Reaction of alcohol with phosphorus tribromide
Solution
The splitting of chemical bonds is known as bond cleavage or bond fission. Basically, it is referred to as dissociation; when a molecule is cleaved into two or more fragments. They are classifications for bond cleavage: homolytic and heterolytic.
Complete answer:
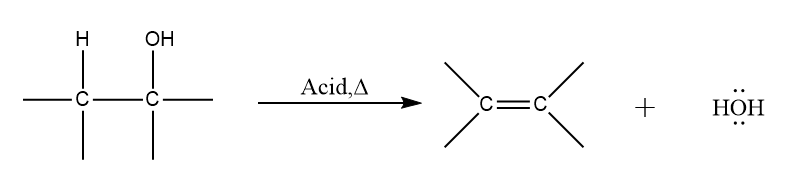
Dehydration of alcohol to yield alkenes: Alcohols undergo E1or E2 mechanisms to lose water and form a double bond; this process is known as dehydration of alcohols. This process is generated alkene by heating of the alcohol in the presence of a strong acid. Thus, it involves the cleavage of C−O bond.
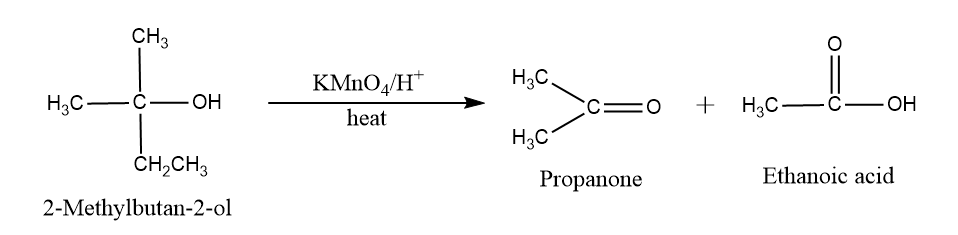
Oxidation reaction of alcohol: In tertiary alcohol, there is no oxidation occur but in presence of KMnO4, cleavage of C−C bond takes place resulting in two acids in which C−O bond remains uncleaved.
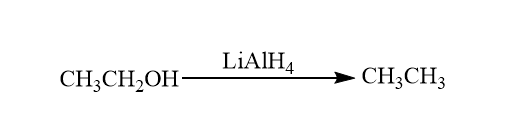
Reduction reaction of alcohol: Alcohols form tosylates undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with hydrides like lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4,akaLAH). This process is the reduction of alcohol to alkanes. So, it also involves the cleavage of C−OH bond.
Reaction of alcohol with phosphorus tribromide: When alcohol reacts with phosphorus tribromide, bromoalkanes are formed. When we use phosphorus (III) bromide the alcohol is heated under reflux with a mixture of red phosphorus and bromine. The phosphorus reacts with the bromine to give phosphorus (III)halide. This reaction also involves the cleavage in the C−OH bond.
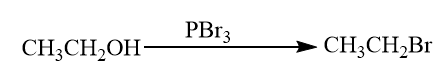
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:
It is important to remember that in primary and secondary alcohols there are C−H bonds thus it forms aldehydes or carboxylic acid and ketones respectively. Whereas in tertiary alcohol there are no C−H bonds so there is cleavage in C−O bonds.
