Question
Question: In which of the following liquid pairs, there is contraction in volume on mixing? A. \( CHC{l_3} +...
In which of the following liquid pairs, there is contraction in volume on mixing?
A. CHCl3+C6H6
B. H2O+HCl
C. H2O+HNO3
D. H2O+C2H5OH
Solution
Hint : Raoult’s law- It expresses a relationship between mole fraction and partial pressure of the volatile liquids. According to this law, the mole fraction of a solute in the solution is directly proportional to its partial pressure. The solutions are categorized into two categories on the basis of Raoult’s law i.e., ideal solution and non-ideal solution.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When after mixing the solution, change in enthalpy is not equal to zero or expansion or contraction in volume of the mixture is observed, then it is said to be a non-ideal solution. Two types of deviations are observed in non-ideal solutions which are as follows:
Case-1: When expansion of the volume of mixture takes place, then it is said to be a positive deviation. In this condition, the intermolecular force of attraction of mixture is weaker than the original liquids i.e., solute-solvent forces are weaker than solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions, therefore on liquids require to absorb heat to form a mixture i.e., it is an endothermic process.
Change in enthalpy of the mixture is greater than zero i.e., ΔmixH>0 and expansion in volume of mixture is observed i.e., ΔmixV>0 .
Examples of positive deviation are as follows:
1. H2O+C2H5OH
2. acetone and ethanol
Graphically, positive deviation in solutions is shown as follows:
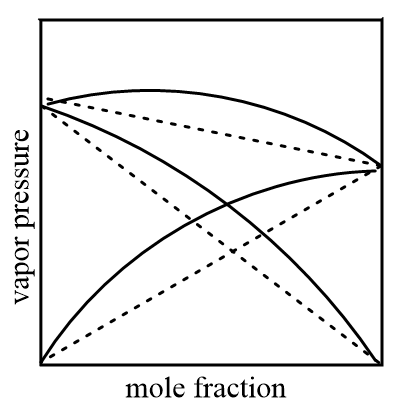
Case-2: When the contraction of the volume of mixture takes place, then it is said to be a negative deviation. In this condition, the intermolecular force of attraction of mixture is stronger than the original liquids i.e., solute-solvent forces are stronger than solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions, therefore on liquids release heat to form a mixture i.e., it is an exothermic process.
Change in enthalpy of the mixture is less than zero i.e., ΔmixH<0 and contraction in volume of mixture is observed i.e., ΔmixV<0 .
Examples of negative deviation are as follows:
1. CHCl3+C6H6
2. H2O+HCl
3. H2O+HNO3
Graphically, negative deviation in solutions is shown as follows:
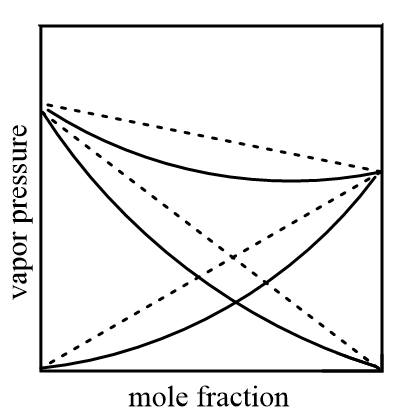
Hence, options (A), (B) and (C) are the correct answers.
Note :
It is important to note that in case of ideal solutions, the change in enthalpy of mixing of solutions is zero i.e., ΔmixH=0 and the total volume of the mixture must be equal to the summation of volume of solute and solvents i.e., ΔmixV=0 . Examples of the ideal solution are benzene and toluene, chlorobenzene and bromobenzene, etc.
