Question
Question: In triangle ABC, right-angled at B, if \(tan{\rm{A}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\), find the value of: ...
In triangle ABC, right-angled at B, if tanA=31, find the value of:
i) sinAcosC+cosAsinC
ii) cosAcosC−sinAsinC
Solution
Use the right-angle triangle Pythagoras theorem. Find the values of sinAcosC+cosAsinC and cosAcosC−sinAsinC. Right angle means the angle is 90∘. It consists of six trigonometric ratios such as sin,cos,tan,cot,sec and cosec.
Complete step by step solution:
We know from the problem that tanA=31.
With the help of above information we can draw the right-angle triangle as we know that tan A is the ratio of perpendicular and base of a right angled triangle.
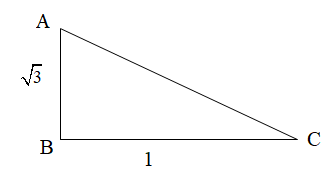
Now, apply the right-angle triangle Pythagoras theorem for the above triangle.
(Hypotenuse)2=(Height)2+(Base)2 AC2=AB2+BC2
Substitute the values from the above diagram AB=3 and BC=1 in AC2=AB2+BC2.
AC2=AB2+BC2 =(3)2+(1)2 =3+1 =4
We can take the square root of the above equation.
AC=4 =2
Hence, the hypotenuse of the triangle from the above result is 2.
Now we also calculate the value of sinA from the formula below.
sinA=HypotenuseBase =ACBC =21
Hence, the value of sinA from the above result is 21.
Now, we also calculate the value of cosA from the formula below.
cosA=HypotenuseHeight =ACAB =23
Hence, the value of cosA from the above result is 23.
Now, calculate the value of sinC:
sinC=HypotenuseBase =ACAB =23
Hence, the value of sinC is 23.
Now, calculate the value of cosC:
cosC=HypotenuseHeight =ACBC =21
Hence, the value of cosC is 21.
(i) Solve the trigonometric relation sinAcosC+cosAsinC.
Substitute the values sinA=21,cosA=23,sinC=23,andcosC=21 in sinAcosC+cosAsinC.
sinAcosC+cosAsinC=(21)(21)+(23)(23) =41+43 =44 =1
Hence, the value of the trigonometric relation sinAcosC+cosAsinC is 1.
(ii) Solve the trigonometric relation cosAcosC−sinAsinC.
Substitute the values sinA=21,cosA=23,sinC=23,andcosC=21 in cosAcosC−sinAsinC.
cosAcosC−sinAsinC=(23)(21)−(21)(23) =43−43 =0
Hence, the value of the trigonometric relation cosAcosC−sinAsinC is 0.
Note: Here we use the Pythagoras theorem to solve the trigonometric values such as sinA and cosA. The trigonometric values cosec, sec and cot are the opposite values of sin, cos and tan respectively.
