Question
Question: In triangle ABC, AD is perpendicular to BC, \(\sin {\text{B}} = 0.8\), BD = 9 cm and \(\tan {\text{C...
In triangle ABC, AD is perpendicular to BC, sinB=0.8, BD = 9 cm and tanC=1. Find the length of AB.
Solution
Hint-Hint- Here, we will proceed by drawing the figure corresponding to the problem statement and then, we will use the identity to find cosB which will eventually give the value of the length AB.
Complete step-by-step answer:
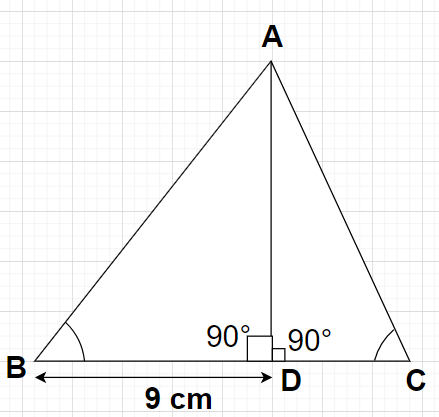
In △ABC, sinB=0.8, BD = 9 cm and tanC=1
AD is the perpendicular drawn from point A to side BC of the triangle ABC which will divide the triangle ABC into two right angled triangles with right angle at vertex D.
As we know that (sinθ)2+(cosθ)2=1
For angle B using the above identity, we can write
(sinB)2+(cosB)2=1
By substituting sinB=0.8 in the above equation, we get
⇒(0.8)2+(cosB)2=1 ⇒(cosB)2=1−(0.8)2 ⇒(cosB)2=1−0.64 ⇒(cosB)2=0.36 ⇒cosB=±0.36 ⇒cosB=±0.6
In any right angled triangle, according to the definition of cosine trigonometric function, we have
cosθ=HypotenuseBase
Using the above formula, we can write
cosB=ABBD ⇒AB=cosBBD
By substituting BD = 9 cm and cosB=±0.6 in the above equation, we get
⇒AB=±0.69
Here, we will be considering only the positive value of cosine of angle B because the length of the side of any triangle is always positive. So, cosB = -0.6 is neglected.
⇒AB=0.69=690 ⇒AB=15 cm
Therefore, the length of side AB of the triangle is 15 cm.
Note- In this particular problem, we can also find the length AD using the Pythagoras Theorem in triangle ABD i.e., (Hypotenuse)2=(Perpendicular)2+(Base)2⇒(AB)2=(AD)2+(BD)2. Also, using tanC=CDAD we will get the length CD and for the length AC we will use Pythagoras Theorem in triangle ACD i.e., (AC)2=(AD)2+(CD)2.
