Question
Question: In the reaction the product E is: 
(A)
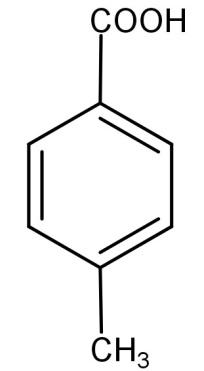
(B)
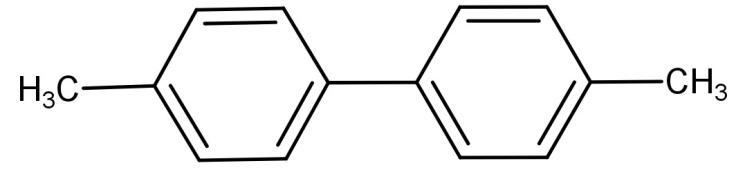
(C)
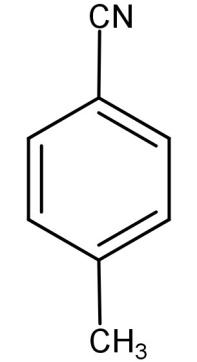
(D)
Solution
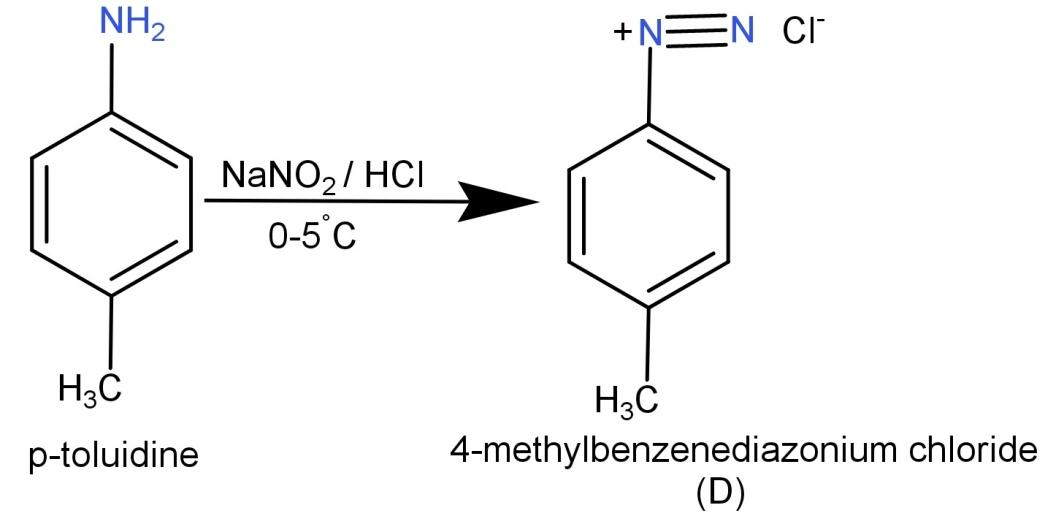
The given initial compound is p-toluidine and is a primary amine. The reactant NaNO2/HCl causes diazotization of the primary amine and leads to the formation of its corresponding diazonium salt. Then its reaction with CuCN or KCN causes the replacement of the diazonium group with the cyano group.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we need to go step by step for each reactant and first find D and then E.
-So, let us begin by finding D.
We know that the initial given compound is p-toluidine (H3C−C6H4−NH2) and it is reacted with NaNO2/HCl which are responsible for diazotization reaction.
The diazotization reaction is a reaction where a primary aromatic amine is converted to its corresponding diazonium salt by the use of nitrous acid and some other acid.
So, p-toluidine (H3C−C6H4−NH2) on reaction with NaNO2/HCl, leads to the formation of its corresponding diazonium salt which is compound (D). This compound (D) is 4-methyl benzenediazonium chloride. The reaction is shown below:
Now (D) 4-methylbenzenediazonium chloride is reacted with CuCN or KCN. CuCN or KCN has the ability to replace the diazonium group with the cyano group. So when we react with 4-methyl benzenediazonium chloride with CuCN or KCN it replaces the diazonium group with cyano group which leads to the formation of 4-methyl benzonitrile. Hence the final product (E) is 4-methyl benzonitrile. The reaction is shown below:
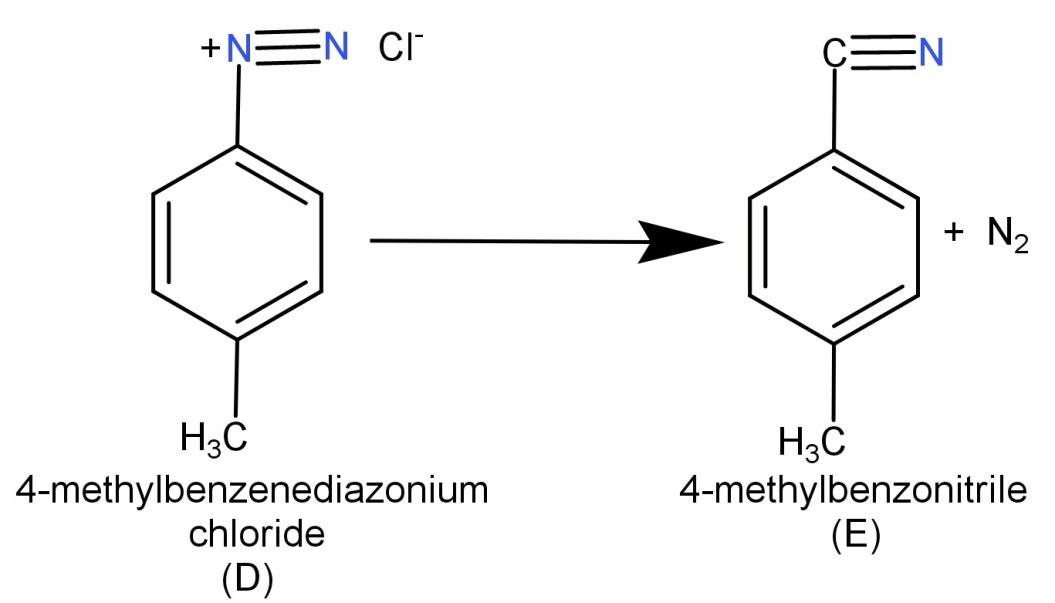
-Hence we can conclude that (E) is 4-methyl benzonitrile.
(C)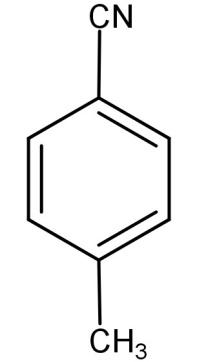
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The diazonium salts are unreactive and hence serve as important synthetic reagents for the formation of dyes and in organic substituents. They can undergo coupling reactions for the formation of azo dyes and also electrophilic substitution reactions for the introduction of functional groups.
