Question
Question: In the reaction sequence\(CH=CH+CH=CH\xrightarrow[N{{H}_{2}}Cl]{CuCl}\left( A \right)\xrightarrow{HC...
In the reaction sequenceCH=CH+CH=CHCuClNH2Cl(A)HCl(B):
(B) will be:
(a) 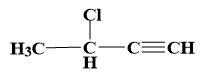
(b) 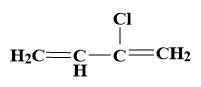
(c) 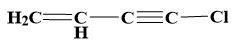
(d) 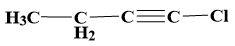
Solution
To find ‘B’, we need to first evaluate for ‘A’. After knowing ‘A’ we will reach ‘B’ easily, as there will only be the addition reaction of HCl on ‘A’.
Also, only one component will be the answer from all the options.
Complete step by step answer:
We will directly see what type of reaction is mentioned here and what products will be produced.
The given molecule is acetylene which then reacts with ammonium chloride in presence of cuprous chloride to form CH2=CHC≡CH.
The reaction can be explained as:
2HC≡CHNH4ClCuClCH2=CHC≡CH
Here, a molecule of acetylene is added to the triple bond of another acetylene molecule but-1-en-3-yne.
Now, but-1-en-3-yne when added to one equivalent of HCl, addition reaction takes place.
Mechanism consists of electrophilic addition of HCl to alkyne to give halogen substituted alkene. Here, molecules have double bonds along with triple bonds. But the addition reaction will proceed in a way where the formed product is stable and the electronic density is minimised over the cloud.
So, HCl will add along the triple bond to form halogen substituted alkene as a stable product. The reaction can be given as:
CH2=CH−C≡CHH+CH2CH−C+=CH2Cl−CH2=CH−C(Cl)=CH2
Thus, we can see that but-1-en-3-yne reacts with HCl to give electrophilic addition reaction forming product as 2-choloro-buta-1, 3-diene.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Do note that the other options have triple bonds in presence of halogen and hydrogen atoms within the molecule. We could have concluded that these are unstable and could reach the required answer.
But we need to go step by step and then conclude the answer. So, we got a stable product of the given reaction i.e. ‘B’ is 2-choloro-buta-1, 3-diene.
