Question
Question: In the reaction \[{C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5} + CO\xrightarrow[{{{150}^O}C}]{{B{F_3},500atm}}X\]. What is ...
In the reaction C2H5OC2H5+COBF3,500atm150OCX. What is X?
1.Diethyl carbonate
2.Ethyl carbonate
3.Diethyl peroxide
4.Ethyl propionate
Solution
Ethers behave as Lewis bases and form coordination complexes with Lewis acids such as BF3. They are known as etherates. Because of the ability of ethereal oxygen to coordinate with the electron deficient species they are used as solvents in preparations of many organometallic compounds such as Grignard reagent.
Complete answer:
The reaction given above is a reaction involving carbon monoxide. Ethers react with carbon monoxide at very high pressure and high temperature to form esters.
Here the BF3 first attacks the lone pair of the oxygen and thus makes it easy for the carbon monoxide molecule to attack the hydrocarbon part. They will react and form the carbonyl part of the ester. Now the alkoxy ion will attack the carbonyl carbon and thus there will be ester formation.
This will give us an ester.
From the above options we know that the ester will be Ethyl propionate.
The structure of the product is given as below-
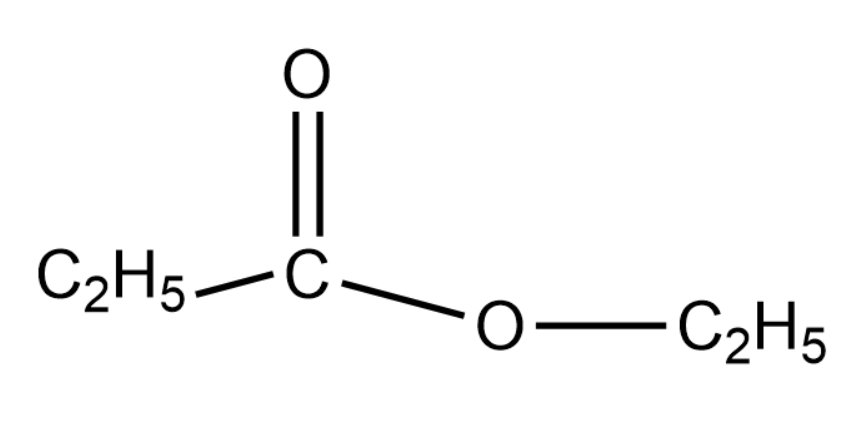
Thus we can say the correct option for this question will be option (4).
Note:
Ethers are widely used as solvents for various organic compounds and reactions, suggesting that they are relatively unreactive. With the exception of the alkanes, cycloalkanes and fluorocarbons, ethers are the least reactive, class of organic compounds. Ethers are less reactive because of the absence of polarity in the molecule. There is no partial positive charge as we observe in carbonyl carbon. So nucleophiles interact with ethers without any reactions taking place.
