Question
Question: In the nephron, water absorption is maximum in A. Proximal convoluted tubule B. Loop of Henle ...
In the nephron, water absorption is maximum in
A. Proximal convoluted tubule
B. Loop of Henle
C. Glomerulus
D. Distal convoluted tubule
Solution
The kidney is an organ that forms a part of the human excretory system found in the human body. They perform the roles of osmoregulation, urine formation, and balance of the acid-base. The nephron is the smallest unit and is known as the functional kidney unit.
Complete answer:
The human kidney is reddish-brown in color and is located in the retroperitoneal space on the right and left. Kidneys consist of the smallest structural and functional unit of the kidney, the nephron. The kidney consists of two parts, called the medulla, and the Nephron cortex is responsible for the production of urine in the human body. The nephron consists of two sections known as the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule. The renal corpuscle is made up of a collection of capillaries called the glomerulus that is surrounded by a cup-shaped structure called the capsule of the bowman. The renal tubule begins with the capsule and ends up in the cortex, the outer region of the kidney. The renal tubule consists of PCT, Henle loop, and DCT. In the inner portion of the kidney, called the medulla, the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), distal convoluted tubule (DCT), and Henle loop are located, while the bowman's capsule is found in the outer cortex region of the kidney. 1. filtration 2. Reabsorbency and 3. Secretion is the urine forming process. In the renal corpuscle, filtration occurs, involving the filtration of large protein molecules, while small molecules are filtered to form ultrafiltrate, which ultimately forms the urine. In PCT, reabsorption involves absorbing ions, molecules, and water into the peritubular capillary that are required for homeostasis to be preserved by the body. Henley's ascending loop consumes the remaining necessary electrolytes, allowing the urine concentration to be hypotonic. The urine in the DCT area is, therefore, hypotonic. The opposite of reabsorption is secretion. This includes creatinine, medicines, hydrogen ions, and urea being secreted from the blood into the collecting duct. 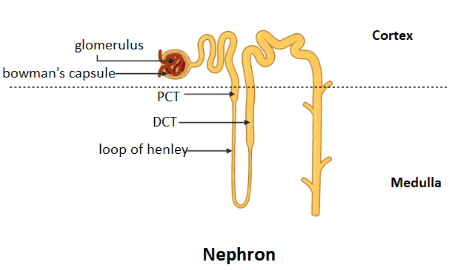
So, option A) is the correct option.
Note: The urine forms water and waste that is not reabsorbed by renal tubules. The glucose and blood components of sugar are not present in urine. Renal tubule dysfunction is unable to absorb glucose and is thus found in the urine. This disease is known as diabetes mellitus.
