Question
Question: In the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction, the carboxylic acids are halogenated at _____ position by usi...
In the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction, the carboxylic acids are halogenated at _____ position by using _______ and _________.
A. α , NaOH, iodine
B. α, phosphorus, halogen
C.β, phosphorus, H2O
D. β, PCl5, NaOH
Solution
We know that addition of halogen to a compound is termed as halogenation. Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction is a reaction in which a carboxylic acid is halogenated.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that alpha carbon is the carbon which is bonded to the carbonyl group. Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction is the reaction in which alpha carbon of the carboxylic acid is halogenated. In this reaction, carboxylic acid possessing alpha hydrogen is halogenated at the alpha position on reacting with bromine or chlorine in the presence of fewer quantities of red phosphorus to result in α-halo carboxylic acid. The HVZ reaction can be represented as follows:
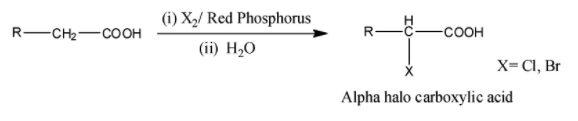
From the above reaction, it is concluded that in Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction, an carboxylic acid having alpha carbon is when halogenated in presence of phosphorus, gives an alpha halo carboxylic acid.
So, the correct option is B, that is, lactic acid.
Additional Information: Reactions of carboxylic acid:
1)Carboxylic acid can be reduced to primary alcohol by lithium aluminium hydride or by diborane. The reduction of functional groups such as ester, nitro, halo etc. is not easy by diborane.
2) Carboxylic acid loses carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salt is heated with soda lime (The ratio of NaOH and CaO in the ratio of 1:3).
Note: The Hell Volhard reaction is only used for halogenations of carboxylic acid containing alpha hydrogen atoms. If no alpha hydrogen atoms are present, the HVZ reaction is not used to produce alpha halo carboxylic acid.
