Question
Question: In the given figure, lines XY and MN intersect at O. If \(\angle POY = {90^ \circ }\) and a:b = 2 : ...
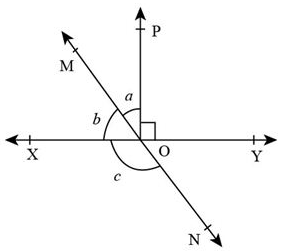
In the given figure, lines XY and MN intersect at O. If ∠POY=90∘ and a:b = 2 : 3, then ∠XON is equal to……..
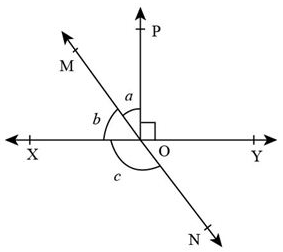
A. 126∘
B. 30∘
C. 90∘
D. 180∘
Solution
Hint:For solving this question, we use the concept of linear pair of angles. We will use axiom1 of linear pair of angles for finding out the value of a and b. As given a:b = 2:3, a = 2x, b = 3x, adding a and b and ∠POYsum should be equal to 180∘. Similarly applying axiom1 on b and c we will be able to find the value of angle ∠XON.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Linear pair of angles: If non common arms of two adjacent angles form a line, then these angles are called linear pairs of angles. There are basically two axioms for linear pair of angles known as linear pair axioms they are as follow:
Axiom1: If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of two adjacent angles so formed is 180°i.e, the sum of the linear pair is 180°. Axiom2: If the sum of two adjacent angles is 180° then the two non common arms of the angles form a line.
Given,
∠POY=90∘….. (1)
a:b=2:3….. (2)
Let the common ratio between a and b be x, therefore, a = 2x, b = 3x.
According to the question: ∠POY+∠POX=180∘….. (3) [By linear pair axiom]
Given, ∠POX=a+b….. (4)
Substituting equation (4) in equation (3), we get,
⇒∠POY+ a + b = 180∘….. (5)
Substituting equation (1) in equation (5), we get,
⇒90∘+ a + b = 180∘
⇒a + b = 90∘ .....(6)
Substituting value of a = 2x and b =3x in equation (6), we get,
