Question
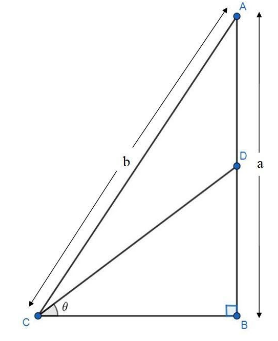
Question: In the given figure, \(AD = DB\) and \(\angle B\) is a right angle. Determine: \({\sin ^2}\theta +...
In the given figure, AD=DB and ∠B is a right angle. Determine:
sin2θ+cos2θ
Solution
Use the given data AD=DB to find the length of DB and apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC to find BC. Use the length DB and BC to find the hypotenuse of the triangle BCD using Pythagoras theorem and then find the trigonometric ratios to approach the desired result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have given that AD=DB and ∠B is a right angle.
We can use the given data,
AB=a
AB can be break in two parts as AD and DB, so it can be express as:
AD+DB=a
It is also given that AD=DB, so we have from the above equation:
AD+AD=a
2AD=a
AD=2a
Thus, we have the conclusion that:
AD=DB=2a.
Now, apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC, then we have
AC2=AB2+BC2
Substitute the value of AB=a and AC=b into the equation, then we obtain
b2=a2+BC2
Solve the equation for the value of BC,
⇒BC2=b2−a2
⇒BC=b2−a2
Now, we have in the ΔBCD:
Base (BC)=b2−a2 and Perpendicular(BD)=2a
Now, apply the Pythagoras theorem in ΔBCD, so we have
BC2+BD2=CD2
Substitute the value of BC and BD into the equation:
(b2−a2)2+(2a)2=CD2
⇒CD2=b2−a2+4a2
Simplify the equation:
⇒CD2=44b2−4a2+a2
⇒CD2=44b2−3a2
⇒CD=24b2−3a2
Now, we have in the ΔBCD:
Base (BC)=b2−a2 , Perpendicular (BD)=2a and the hypotenuse (CD)=24b2−3a2
Now, use the trigonometric ratio in ΔBCD,
sinθ=CDBD
Substitute the values of BD and CD, so we have
sinθ=24b2−3a22a
sinθ=4b2−3a2a
Using the trigonometric ratio:
cosθ=CDBC
Substitute the values of BC and CD, so we have
cosθ=24b2−3a2b2−a2
cosθ=4b2−3a22b2−a2
We have to find the value of sin2θ+cos2θ, so substitute the value of sinθ and cosθ into the equation:
sin2θ+cos2θ=(4b2−3a2a)2+(4b2−3a22b2−a2)2
⇒sin2θ+cos2θ=4b2−3a2a2+4b2−3a24(b2−a2)
⇒sin2θ+cos2θ=4b2−3a2a2+4b2−4a2
⇒sin2θ+cos2θ=4b2−3a24b2−3a2
⇒sin2θ+cos2θ=1
Therefore, the value of sin2θ+cos2θ is 1.
Note: The Pythagoras theorem says that when one of the angles of the triangle is a right angle then the square of the hypotenuse of the triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the perpendicular and base of the triangle.
