Question
Question: In the given electric circuit, the current flowing through the 3ohm resistor is 1ampere. Find the vo...
In the given electric circuit, the current flowing through the 3ohm resistor is 1ampere. Find the voltage of the battery and the circuit drawn from it.
Solution
Hint: In a parallel combination of resistors, the current divides but voltage between the terminals is the same and reciprocal of the total resistance is the sum of the reciprocal of individual resistances.
In series combination of resistors voltage divides between two resistors but same current flows through them and effective resistance is the sum of the two resistances.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider circuit diagram, where R1=2Ω,R2=3Ω and R3=6Ω. Let I2=1A is the current flowing through R2 as given in the question.
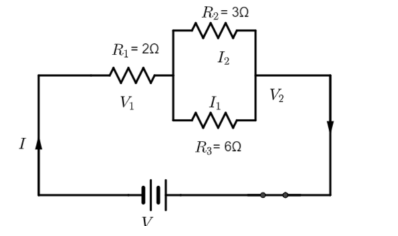
Now we have to find I and V which are total current and potential respectively.
Now first part to find total current I, we have,
I=I1+I2 …….. (1)
we already know I2 as it is given in question we have to find I1
To find I1 :
I1=R3V2 ….. (2)
the same voltage V2 flows through R3 as they are aligned parallel to each other.
but we don’t know V2, it can be determined by using the formula:
V2=I2R2 (Ohm’s law)
on substituting values of resistance and current we get,
V2=1×3=3V
On substituting V2 in (2) we get
I1=R3V2=63I1=21A=0.5A
Now we know both I1andI2 substituting in (1) we get
I=1+0.5I=1.5A
Thus, total current flowing through the circuit is found.
Now second part to find total potential V, we have,
V=V1+V2 …… (3)
We know what is V2 but have to find V1 ,
V1=IR1
on substituting I and R1 we get
V1=1.5×2V1=3V
on substituting values in (3)
V=3+3V=6V
Thus, total potential of the circuit is found.
Note: Students should remember all the above formulas to solve this type of question.
Students may get confused about V and I which is constant, and which will vary when connected in series and parallel. Always remember that in series combination of resistors voltage divides current remains same between resistors and in parallel combination, the current divides but voltage remains constant.
