Question
Question: In the given diagram, parts labelled as A, B, C, D, E and F are respectively identified as 
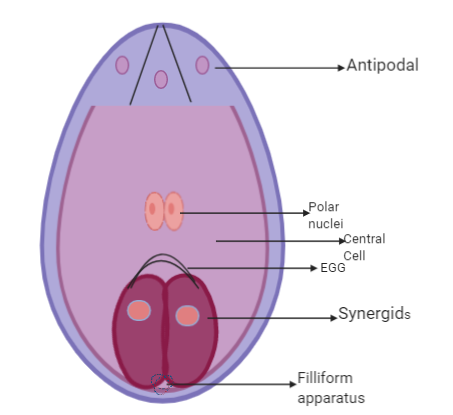
A) Synergids, polar nuclei, central cell, antipodals, filiform apparatus and egg
B) Polar nuclei, egg, antipodals, central cell, filiform apparatus and synergids
C) Egg, synergids, central cell, filiform apparatus, antipodals and polar nuclei
D) Central cell, polar nuclei, filiform apparatus, antipodals, synergids and egg
Solution
The characteristic features of angiosperms is the fusion of a gametophyte with two male gametes, also called double fertilisation. At the end of the micropyle end, which is collectively called an egg apparatus, an embryo bag consists of three cells.
Complete answer: The embryo has a normal distribution of cells in angiosperms. There are 2 synergies and one egg cell in the egg apparatus. These synergistic cells possess the micropylar tip called filiform devices with cell thickenings. Set up in this system, the pollen pipes play a major role in synergy. Excluding the egg machinery, the chalazal end also has three cells known as the antipodal cells. A wide central cell with two polar nuclei is also available. Thus, there is a typical angiosperm embryo bag containing 7 cells, which consists of 8 nuclei. The stigma produces a pollen tube with two male gametes and stretches into the ovarium in style. Dual fertilisation in angiosperm-pollen grains germinates.
The female gametophyte, i.e., the embryo sac is a practical super shop. It is subjected successively to three mitotic divisions, creating an eight nucleate embryo sac, which is seen at maturation to be 7 that of 8 nuclear embryo sacs (One moves towards the end of micropylar and the other moves towards the end of chalazal.). At the end of the chalaza, three of the four nuclei are segregated to antipodal cells. At the end of the micropylar, three of the four nuclei differentiate and form one egg cell and two synergies. Three nuclei differentiate from each other. Megaspore is the mother cell for women's gametophytic growth. The diagram is a mature embryo-sac in which A points to synergies, B to a polar nucleus, C to a central cell, D to antipodal, E to a filiform apportion and F to an ovary.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Double fertilisation produces endosperm which nourishes the developing embryo. In certain plants, the developing embryo absorbs endosperm entirely before the seed matures, e.g., pea, groundnut and beans.
