Question
Question: In the free-radical chlorination of methane, the chain-initiation step involves the formation of: ...
In the free-radical chlorination of methane, the chain-initiation step involves the formation of:
a.) Hydrogen chloride
b.) Methyl Radical
c.) Chloromethyl radical
d.) Chlorine radical
Solution
Hint: Before attempting this question one should have prior knowledge of the chain mechanism of chlorination of methane by following the three steps of the chain mechanism that includes initiation, propagation and termination to identify the free radical which is formed in the chain initiation step.
Complete step by step solution:
In chemistry, a radical can be understood as an atom, molecule, or ion that has an unpaired valence electron. Although, there are some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals which are highly reactive.
According to the question the chain mechanism is as follows, using the chlorination of methane
Initiation:
The steps involve splitting of a chlorine molecule which then forms two chlorine atoms; this process is initiated by ultraviolet radiation or sunlight.
As we know, chlorine has one unpaired valence electron, which will now act as a free radical.
Propagation:
The second step propagation involves two steps:
The first step occurs when chlorine for a radical or atom approaches methane and forms methane it picks off a hydrogen atom, subsequently leaving a methyl radical behind. This process is endothermic as heat is used.
Now, the second step occurs when the methyl radical that was left finds a Cl2molecule and then it picks off a chlorine atom behind. This process is exothermic as heat is released
Now, the last and final step which is
Termination
In this step, the low concentration of radical which means that propagation is the most likely process, thus, we can say that chlorine atom is much likely to find methane over any other.
Similarly, a methyl radical is much more likely to find Cl2 than anything else. However, now the radical starts to find each other which therefore shuts down the propagation cycle by removing radicals.
Hence, termination happen which of includes these reactions 
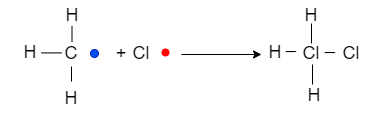
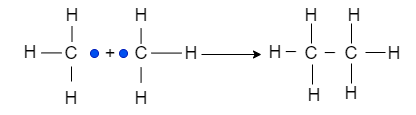
Thus, from the above chain-initiation steps, it is clear that chlorine radical is formed.
Hence, option D is the correct option.
Note: The compound that we came across in the above solution can be defined as a gas which is odorless, colorless and is flammable, It has many uses such as:
- It is used as fuel to make heat and light.
- It is used to manufacture organic chemicals.
- Methane is formed by the decay of natural materials and is common in landfills, marshes, sewers, etc..
