Question
Question: In the following sequence of reactions \[C{{H}_{3}}-CH(N{{H}_{2}})-C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{HN{{O}_...
In the following sequence of reactions
CH3−CH(NH2)−CH3HNO2AoxidationB(i)CH3MgI(ii)H+/H2OC
The compound C formed will be
(A) butanol-1
(B) 2-methylpropan-1-ol
(C) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(D) butanol-2
Solution
The compound C can be determined when we predict the products of the given sequence of reaction. We can see that the reactant is being reacted with nitrous acid, followed by the oxidation of the product and further reacting the product formed with Grignard's reagent.
Complete step-by-step answer: In the given reaction, the reactant is isopropylamine. It is a primary amine. It is a highly flammable organic compound and is an important intermediate in chemical industries.
When primary amines react with nitrous acid, the amine group is replaced by the hydroxyl group to give primary alcohol along with the release of nitrogen gas.
CH3−CH(NH2)−CH3HNO2CH3−CH(OH)−CH3+N2
So, compound A is isopropyl alcohol.
Isopropyl alcohol formed is a secondary alcohol. It is the simplest secondary alcohol and can be used in detergents, disinfectants, and antiseptics. It is also highly flammable.
Now, when secondary alcohol is oxidized, the hydroxyl group and the hydrogen atom are replaced by the carbonyl group to form a ketone
CH3−CH(OH)−CH3oxidationCH3−C(=O)−CH3
So, compound B is acetone.
Acetone is also known as propanone and is the simplest ketone. It is also highly flammable and is a common household product used in nail paint removers and used as paint thinners.
Now, finally, when we react a ketone reacts with Grignard's reagent RMgX in the presence of water and H+ ions, the carbonyl group is replaced by the alkyl group from the Grignard's reagent and the hydroxyl group to form tertiary alcohols.
CH3−C(=O)−CH3(i)CH3MgI(ii)H+/H2OCH3−C(CH3)(OH)−CH3
So, compound C is 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
2-methylpropan-2-ol is also known as tert-butyl alcohol and is the simplest tertiary alcohol. It has a camphor-like odor and is commonly used as solvents.
The final reaction can be written as
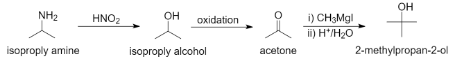
So, in the given sequence of reactions, compound C will be option (C) 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
Note: It should be noted that all of the following reactions, reaction with nitrous oxide, oxidation, and reaction with Grignard's reagent are dependent on the degree of the functional group amine, hydroxyl, or carboxylic group. The products formed changes with the change in the degree of the functional group.
