Question
Question: In the following reaction, the product(s) formed is (are):  formed is (are):
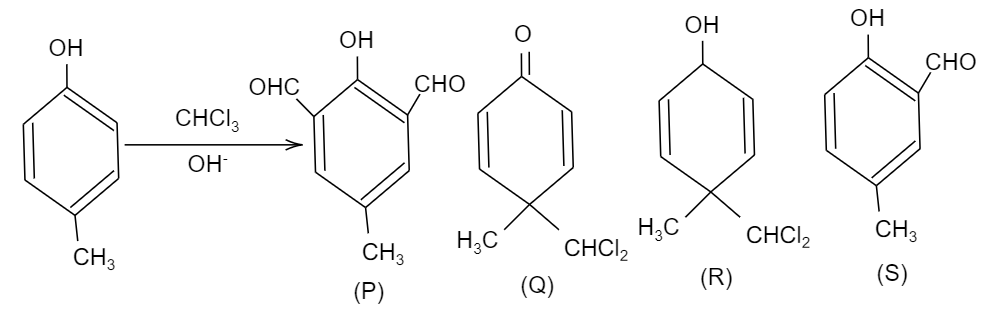
A. P(major)
B. Q(minor)
C. R(minor)
D. S(major)
Solution
The given questions about the major and minor products formed after reaction. So, to get the appropriate answer for the question, we have to consider the Riemer Tiemann reaction mechanism. So, look upon what happens when the compound given undergoes this reaction and see what are the products formed.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question, the compound given is named as 4-methyl phenol and it is being reacted with CHCl3 and OH−. So, before proceeding to find what are the products formed, let us look upon what is Riemer Tiemann reaction.
Riemer Tiemann reaction is a type of substitution reaction, which is named after chemists Karl Reimer and Ferdinand Tiemann. The reaction is usually used for the ortho-formylation of phenols.
So, when phenols i.e. C6H5OH is treated with chloroform i.e. CHCl3 in the presence of NaOH(sodium hydroxide), an aldehyde group (−CHO) is introduced at the ortho position of the benzene ring leading to the formation of o-hydroxybenzaldehyde as the major product. And this reaction is popularly known as the Reimer Tiemann reaction.
So, here in the given question, when 4-methyl phenol reacts with chloroform i.e. CHCl3 and sodium hydroxide having hydroxyl ion, i.e. OH−, an aldehyde group will be attached to the ortho position of the compound due to ortho-formylation of the compound. This product is the major product and it is named as 2−hydroxy−5−methyl−benzaldehyde. While. We should also see that there is significant charge density at the fourth position of the compound, so there will be an attack of the nucleophile at the fourth position, forming the minor product.
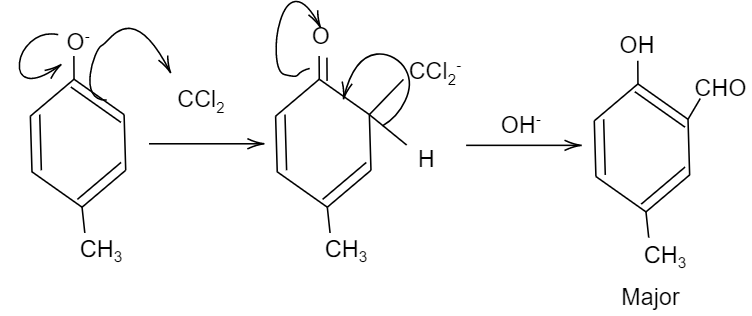
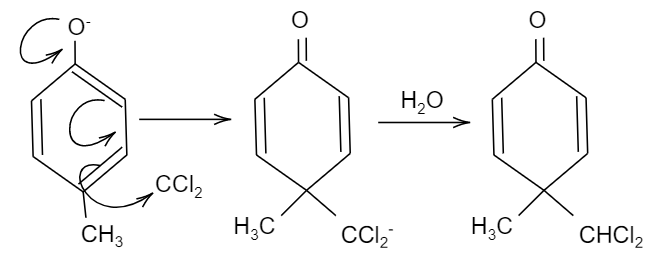
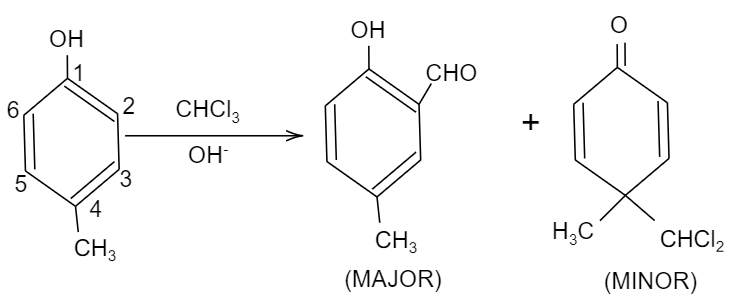
The products formed are Q as minor and S as minor.
So, the correct answer is “Option B and D”.
Note: Remember, the Reimer Tiemann reaction is used for the ortho formylation of the phenols. It is effective for other hydroxy-aromatic compounds, such as naphthols, etc. Electron rich heterocycles such as pyrroles also react using this mechanism.
