Question
Question: In the figure shown ‘\(P\)’ is a plate on which a wedge \(B\) is placed and on \(B\), a block \(A\) ...
In the figure shown ‘P’ is a plate on which a wedge B is placed and on B, a block A of mass m is placed. The plate is suddenly removed and the system of B and A is allowed to fall under gravity. Neglecting any force due to air on A and B, the normal force on A due to B is
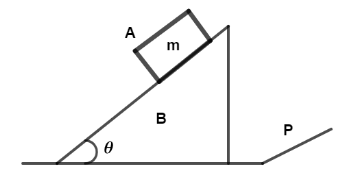
A. cosθmg
B. mgcosθ
C. Zero
D. cosθ2mg
Solution
In physics, when two bodies are in contact with each other, then the perpendicular force between the surface of two bodies is called normal reaction force, in the given question we will first draw the free body diagram and observe various force acting on A and B under free fall of gravity and thus find the magnitude of normal reaction force which is denoted by N.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the free body diagram of the given system consisting of wedges and blocks while falling under gravity. Let θ be the angle between sliding part and bottom of wedge, now weight of block A of mass m acting downward is given by
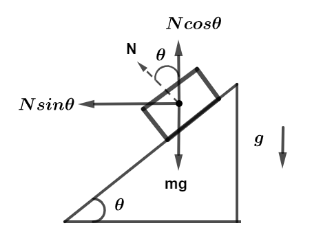
F=mg
Now the reaction force in upward direction from the geometry of diagram can be seen as
FN=Ncosθ Where N is the normal reaction force between block A and wedge B. Since, weight F=mg=0 under the free fall of gravity is always zero so,
By equilibrium of force we get,
F=FN
⇒Ncosθ=mg
Since F=mg=0 we get,
Ncosθ=0
∴cosθ=0
Therefore, the normal reaction force is N=0 between block A and wedge B.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: It should be remembered that, the actual weight of block A of mass m remains mg in its own reference frame but when falling freely under gravity with the contact wedge B, the weight acting on wedge B of block A will be zero as, under free fall, force of gravity gives equal and opposite force in upward direction hence, wedge will read the weight of block as zero.
