Question
Question: In the experiment ‘Light is essential for photosynthesis’. Why does the undercovered part of the lea...
In the experiment ‘Light is essential for photosynthesis’. Why does the undercovered part of the leaf turn blue-black after putting it in the iodine solution?
Solution
The process through which green plants and certain other creatures convert light energy into chemical energy is known as photosynthesis. Light energy is collected and utilised by green plants during photosynthesis to transform water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic molecules.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis is a process that plants and other organisms utilise to transform light energy into chemical energy that may then be released to power the organism's activities via cellular respiration. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules like sugars and starches, which are created by combining carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis is performed by the majority of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria; these organisms are known as photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is capable of establishing the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, as well as supplying the majority of the energy required for the existence of life.
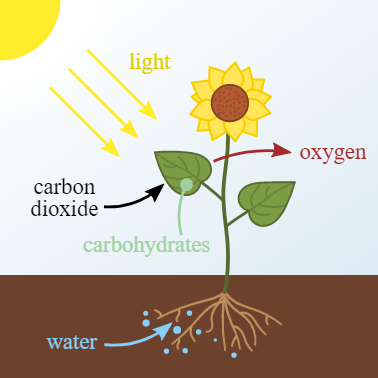
Light is required for photosynthesis in the experiment, and the exposed portion of the leaf absorbs sunlight and performs photosynthesis. As a result of the starch generation, the leaf becomes blue-black after applying iodine to this region. When dilute iodine solution comes into contact with another substance, it changes to a blue-black hue, indicating the presence of starch in that substance.
Note: Photosynthetic creatures are photoautotrophs, which means they can manufacture food directly from carbon dioxide and water with the use of light energy. However, not all organisms employ carbon dioxide as a source of carbon atoms for photosynthesis, these organisms (photoheterotrophs) use organic substances as a source of carbon rather than carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis produces oxygen in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. This is referred to as oxygenic photosynthesis, and it is by far the most prevalent kind of photosynthesis employed by living organisms.
