Question
Question: In the dichromate di-anion: (A) 4 \(Cr-O\) bonds are equivalent (B) 6 \(Cr-O\) bonds are equival...
In the dichromate di-anion:
(A) 4 Cr−O bonds are equivalent
(B) 6 Cr−O bonds are equivalent
(C) All Cr−O bonds are equivalent
(D) All Cr−O bonds are non-equivalent
Solution
The dichromate di-anion has two chromium atoms and seven oxygen atoms. Each chromium atom is attached to three oxygen atoms and one oxygen atom forms a bridge between these chromium atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
The dichromate di-anion means there are two chromate ions and there is −2 charge on the overall molecule. The dichromate di-anion has two chromium atoms and seven oxygen atoms. The formula of dichromate di-anion is Cr2O72−. It is also known as dichromate, dichromate ion, bichromate, etc. The molecular mass of dichromate ions is 215.99 g/mol.
So, there are two chromium atoms in the dichromate ion, and each chromium atom is joined to three oxygen atoms. This means that there are six Cr−O independent bonds. And both these molecules are joined by the same oxygen atom which acts as a bridge. This molecule has a -2 charge on the overall molecule which is because of the charge on two oxygen atoms. Now due to resonance, the six Cr−O bonds have equal length and the charge is on the overall molecule. The bond length of the Cr−O bond lies between the length of a single bond and the length of a double bond.
The structure of the dichromate di-anion can be represented in two forms. These are given below:
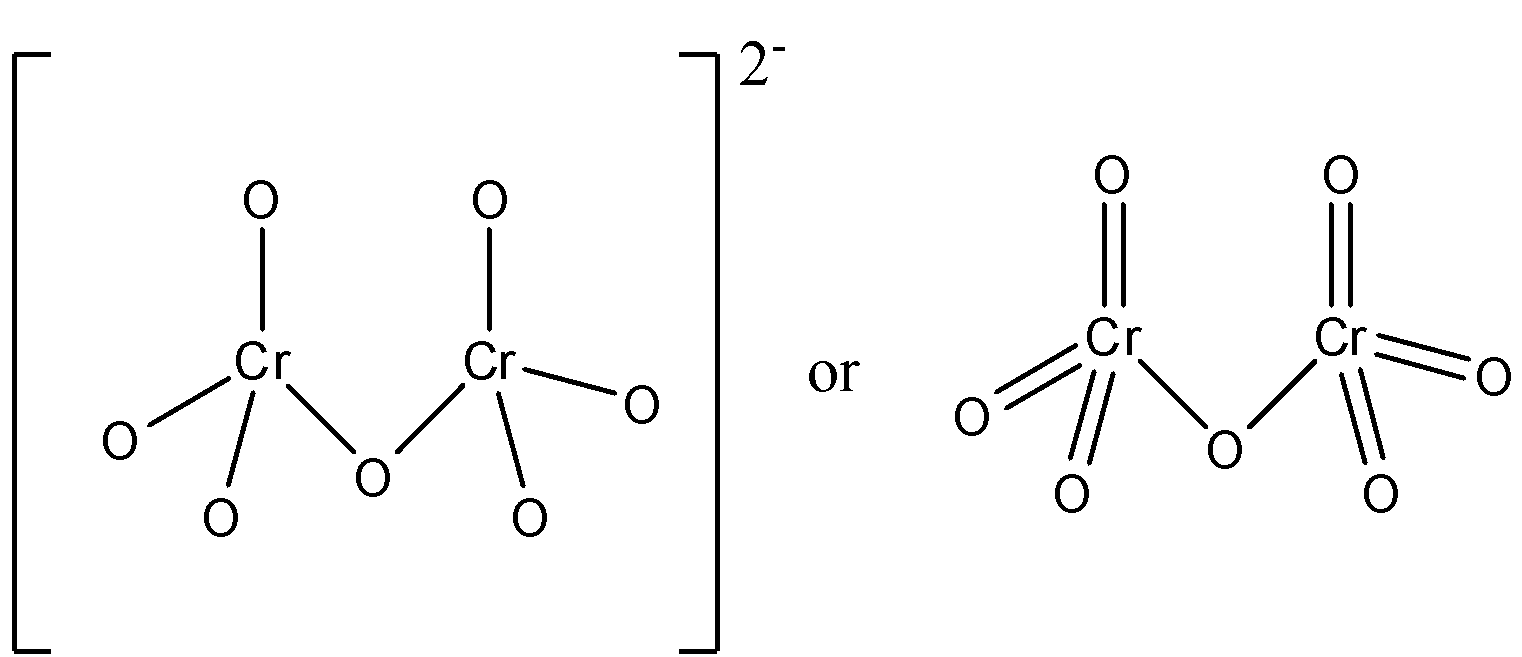
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (B)- 6 Cr−O bonds are equivalent.
Note: The formal charge on the dichromate ion is -2. The exact mass of dichromate ion is 215.85 g/mol. Dichromate ion is basic because it can accept hydrogen ions.
