Question
Question: In the diamond crystal, each carbon atom is linked with carbon atoms? The number of carbon atoms lin...
In the diamond crystal, each carbon atom is linked with carbon atoms? The number of carbon atoms linked is:
A.2
B.4
C.3
D.1
Solution
To answer this question, recall the concept of the crustal structure of the diamond lattice. Diamonds also can be produced synthetically during a high-pressure high-temperature process which approximately simulates the conditions within the Earth’s mantle.
Complete step by step answer:
The four main optical characteristics of diamonds are transparency, luster, dispersion of sunshine, and colour. In its pure carbon form, diamond is totally clear and transparent. Diamonds are the toughest substance known. This beautiful diamond didn’t start because it looks in its final form. Uncut diamonds have greasy lustre and aren't brilliant in the least. But equivalent stones when cut exhibit a high luster. The first object of cutting a diamond is to bring out the hearth and brilliance of the stone. It is the toughest natural substance with the very best thermal conductivity. it's utilized in major industrial applications like cutting and polishing tools. The diamond crystal consists of an atom during which each atom is linked with four other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds. The four surrounding carbon atoms form the four vertices of a daily tetrahedron. Each atom has the toughest natural substance with the very best thermal conductivity. it's utilized in major industrial applications like cutting and polishing tools. The diamond crystal consists of an atom during which each atom is linked with four other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds. The four surrounding carbon atoms form the four vertices of a daily tetrahedron. Each atom has sp3 hybridization. σ bond links a carbon atom with 4 other carbon atoms. The overall structure can be summarized by the figure below:
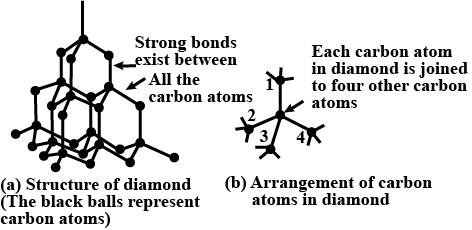
Hence, the right option is option B.
Note:
The diamond lattice (formed by the carbon atoms during a diamond crystal) consists of two interpenetrating face-centered cubic Bravais lattices, displaced along the body diagonal of the cubic cell by a length of one quarter the length of the diagonal.
