Question
Biology Question on Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
In the diagram of T.S. of Stele of Dicot Root, the different parts have been indicated by alphabets; choose the answer in which these alphabets correctly match with the parts they indicate:
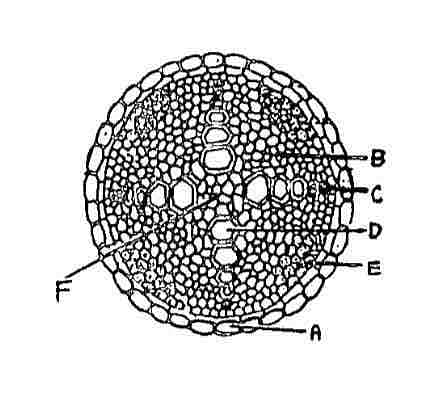
A = Pericycle; B = Conjunctive tissue; C = Metaxylem; D = Protoxylem; E = Phloem; F = Pith
A = Endodermis; B = Conjunctive tissue; C = Protoxylem; D = Metaxylem; E = Phloem; F = Pith
A = Endodermis; B = Conjunctive tissue; C = Metaxylem; D = Protoxylem; E = Phloem; F = Pith
A = Endodermis; B = Pith; C = Protoxylem; D = Metaxylem; E = Phloem; F = Conjunctive tissue
A = Endodermis; B = Conjunctive tissue; C = Protoxylem; D = Metaxylem; E = Phloem; F = Pith
Solution
The correct answer is: A = Endodermis; B = Conjunctive tissue; C = Protoxylem; D = Metaxylem; E = Phloem; F = Pith
In the T.S. of stele of dicot plants, the xylem and phloem are arranged in an X-shape. The parenchyma tissue present between xylem and phloem is called conjunctive tissue.
- Endodermis - These are cells seen in the T.S. of stele of a dicot root without any intercellular spaces.
- Conjunctive Tissue - It separates xylem from phloem.
- Protoxylem - In dicot plants, it is present away from the center.
- Metaxylem - It is situated towards the center.
- Phloem - In dicot roots, xylem and phloem are arranged radially i.e. they are present in different radii.
- Pith - At the center of the dicot roots, a small pith can be seen.
