Question
Question: In the circuit shown, the total current supplied by the battery is 
A. 1A
B. 2A
C. 3A
D. 6A
Solution
We can find the total current supplied by the battery using Ohm’s Law which states that voltage of a battery is the product of the current supplied and the total resistance. To find the total resistance, we need to rearrange the given circuit to understand the series and parallel connections.
Formula used:
Series connection of resistors Req=R1+R2+...+Rn
Parallel connection of resistors Req1=R11+R21+...+Rn1
Ohm’s Law V=IR
Complete step by step answer:
Let us note down the given data,
R1=3Ω , R2=6Ω , R3=4Ω , R4=3Ω , and V=6V
Now, let us name the nodes to understand the series and parallel connections of resistors as shown below,
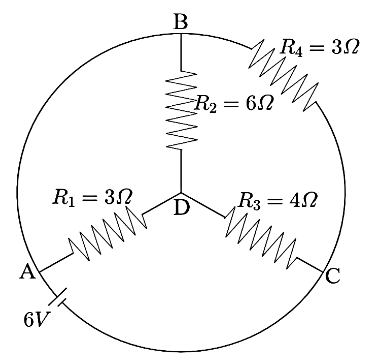
Now, from the figure above, we can see that between the points A and B there is a simple wire. This means that the potential at points A and B is the same. Hence, they can be considered as the same points.
Thus, we can see that the resistors R1 and R2 are connected between the same points and hence, they are said to be connected in parallel connection. Now, the combination of R1 and R2 is directly connected to resistance R3 . Hence, this is a serious connection.
Now, the combination of R1 , R2 , and R3 is connected between the points A and C and so is the resistance R4 . Hence, this is a parallel connection. Hence, the above shown circuit can be redesigned as below,
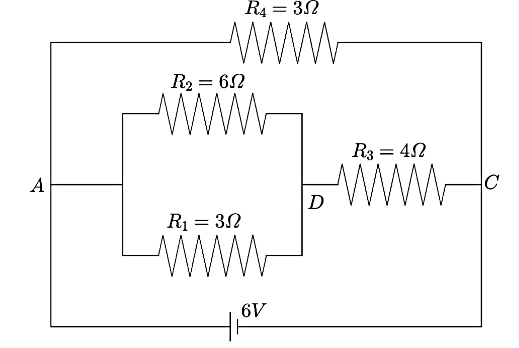
Now, we can see from the above figure that the resistance R1 and R2 are in parallel connection and the equivalent reaction can be calculated as,
R′1=R11+R21
Substituting the given values,
R′1=3Ω1+6Ω1
⇒R′1=6Ω3
Taking the reciprocal on both sides,
⇒R′=36Ω
⇒R′=2Ω
Now, the circuit can be drawn as shown below,
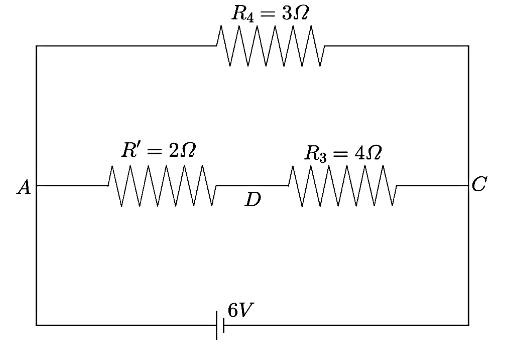
Now, the resistances R′ and R3 are connected in series. Hence, the equivalent resistance can be calculated as
R′′=R′+R3
Substituting the given values,
⇒R′′=2Ω+4Ω
⇒R′′=6Ω
Now, the circuit can be redrawn as shown below,
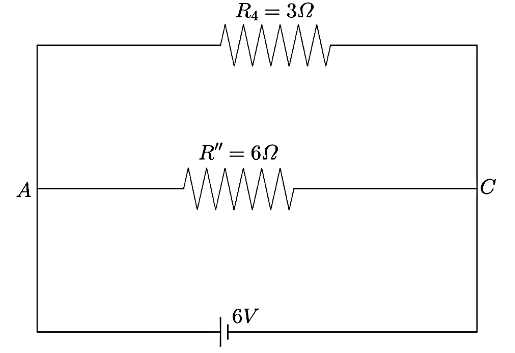
Now, the resistances R′′ and R4 are connected in parallel connection. Hence, the equivalent resistance can be calculated as
Req1=R′′1+R41
Substituting the given values,
Req1=6Ω1+3Ω1
⇒Req1=6Ω3
Taking the reciprocal on both sides,
⇒Req=36Ω
⇒Req=2Ω
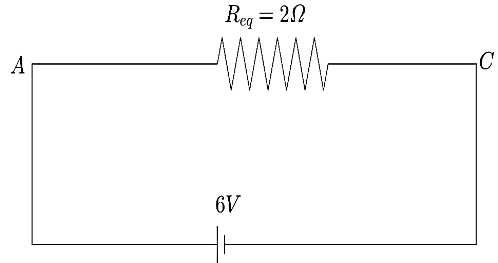
This is the total resistance of the circuit. Now, the total current can be calculated using the Ohm’s Law
V=IR
Substituting the given values,
⇒6V=I(2Ω)
∴I=3A
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: We should note that in this type of problem, we should always start by naming the junctions in the circuit. While naming, if there is no other component other than a simple wire between the two points, then those two points are considered to be the same. We should remember that resistors are said to be in parallel when they are connected between the same two points, and they are said to be in series when they are connected in a line.
