Question
Question: In the circuit shown below, \({V_A}\)and \({V_B}\) are the potential at A and B, R is the equivalent...
In the circuit shown below, VAand VB are the potential at A and B, R is the equivalent resistance between A and B, S1and S2 are switches, and the diodes are ideal
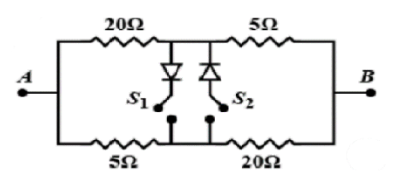
A) If VA>VB, S1 is open and S2is closed then R=8Ω
B) If VA>VB, S1 is closed and S2is open then R=12.5Ω
C) If VA>VB, S1 is open and S2is closed then R=12.5Ω
D) If VA>VB, S1 is closed and S2is open then R=8Ω
Solution
An electric circuit and each component of the circuit are known as an element. The given circuit is connected from the resistance values 20Ω and5Ω.
The ideal diodes are connected from the S1 and S2 switches.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given VA>VB,so current flows from A to B.
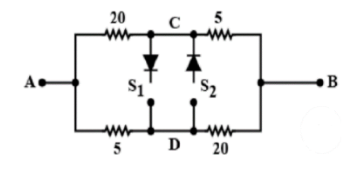
From the below figure when S1 is open and S2is closed
-The diode at S2passes current only from D to C else zero current.
-If the current passes through the diode the voltage will be equal to D and C.
Let us assume that the D and C voltages are equal. Now we can short the S2part.
Now in the equivalent circuit as20Ω>5Ωcurrent flows from D to C.
So it is satisfying the diode property.
Our circuit equivalent circuit will be the above circuit.
So the equivalent resistance =2×(201+51)1Ω
Here we have to take an LCM on the denominator term we get
=2×(201+4)1Ω
Let us add the term we get
=2×(205)1Ω
On dividing the term we get
=2×(41)1Ω
Taking reciprocal of the numerator term and multiply it we get,
=8Ω
Now,S1 is closed and S2is open
-The diode at S1passes current only from C to D or else zero current.
- If current passes through the diode the voltage will be equal to D and C.
-Let us assume that the D and C voltage is equal. Now in the equivalent circuit as 20Ω > 5Ωcurrent has to flow from D to C. From D to C current does not allow. So our assumption is wrong.
We have to treat S1as open.
The equivalent resistance is =220+5Ω
On adding the numerator term we get
=225Ω
Let us divide the term we get
=12.5Ω
Additional information:
Potential difference, when the current flows between two points A and B of an electric circuit.
Where the aggregate resistance connected either in parallel or series is calculated, it is called equivalent resistance. Essentially, either in Series or Parallel is designed in the circuit
Note: A diode that acts like a perfect conductor, ideal diodes, when voltage is applied forward biased and like a perfect insulator, when voltage is applied reverse biased.
So the anode to the cathode when the positive voltage is applied across, the diode conducts forward current instantly.
