Question
Question: In the circuit shown below, the cell has an emf of 10 V and internal resistance of 1 Ohm. The other ...
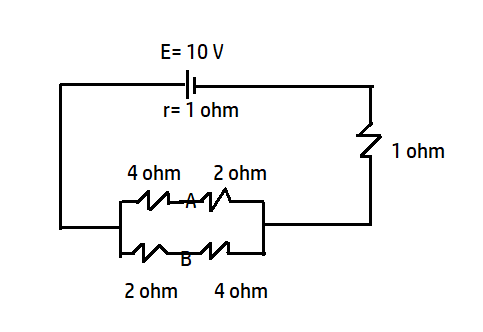
In the circuit shown below, the cell has an emf of 10 V and internal resistance of 1 Ohm. The other resistances are shown. Find the potential difference between point A and B.
Solution
fist of all we need to find the value of current in the two branches containing the point A & B. then by using the Ohm’s law there we can find the value of potential at A and B and then the potential difference can be find out.
Complete step by step answer:
Internal resistance of the battery, r= 1 Ω
The branch containing point A. 4 Ωand 2 Ωare in series, so, net resistance is 6 Ω and for the branch containing 2 Ω and 4 Ω are in series so the net resistance for this branch is 6 Ω. Now both the 6 Ω resistors are in parallel, so, the equivalent resistance is given as R=R1+R2R1R2=6+66×6=3Ω
Now 3 Ω and 1 Ω are in series, so the net resistance of the circuit is 3+1=4 Ω
Total internal resistance in the circuit= 1 Ω
Total external resistance in the circuit=4 Ω
Using ohm’s law I=R+rV=4+110=2A
Now talking about the two branches having points A and B. the resistance of both the branches are equal, so the current in both the branches must be equal and that will be 1A each.
Hence, the potential difference between the points A & B is
