Question
Question: In the circuit shown, a potential difference of \(60V\)is applied across \(AB\). The potential diffe...
In the circuit shown, a potential difference of 60Vis applied across AB. The potential difference between the points M and N is:
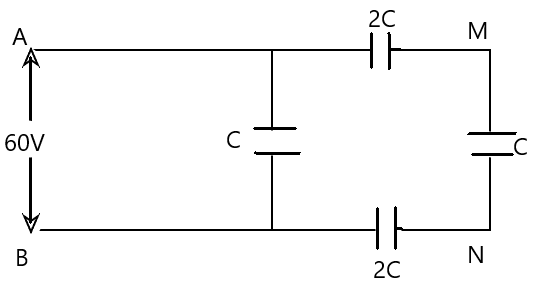
A) 60V
B) 15V
C) 20V
D) 30V
Solution
The charges on the capacitors in series are the same. The electric potential across the capacitors or the combination of the capacitors in parallel are the same.
Complete step by step solution:
When capacitors are in series then the equivalent capacitance can be calculated as,
Ceq1=C11+C21+C31+⋯⋯+Cn1
Here, C1,C2,C3……Cn are the capacitances of the capacitors connected in series, and Ceqis the equivalent value of the capacitance.
When capacitors are in series then the equivalent capacitance can be calculated as,
Ceq1=C11+C21+C31+⋯⋯+Cn1
Here, C1,C2,C3……Cn are the capacitances of the capacitors connected in parallel, and Ceq is the equivalent value of the capacitance.
From the electric circuit given, the capacitors in the right branch are in series.
Let equivalent capacitance of the capacitors in the right branch is C1
Using the formula of the equivalent capacitance in series,
\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
{} & \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}=\dfrac{1}{2C}+\dfrac{1}{C}+\dfrac{1}{2C} \\\
{} & \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}=\dfrac{1+2+1}{2C} \\\
{} & \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}=\dfrac{4}{2C} \\\
{} & \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}=\dfrac{2C}{4} \\\
{} & \therefore {{C}_{1}}=\dfrac{C}{2}\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } \\\
\end{array}
Now, C1 is in parallel with the capacitor on the left branch.
Let Ceq is the equivalent capacitance of the given circuit.
Using the equivalent capacitance in parallel combination,
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{}&{{C_{eq}} = {C_1} + C} \\\
{}&{ \Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = \dfrac{C}{2} + C} \\\
{}&{ \Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = \dfrac{{C + 2C}}{2}} \\\
{}&{\therefore {C_{eq}} = \dfrac{{3C}}{2}{\text{ }}\;{\text{ }}\;{\text{ }}}
\end{array}
The equivalent capacitance of the given electric circuit is 23C
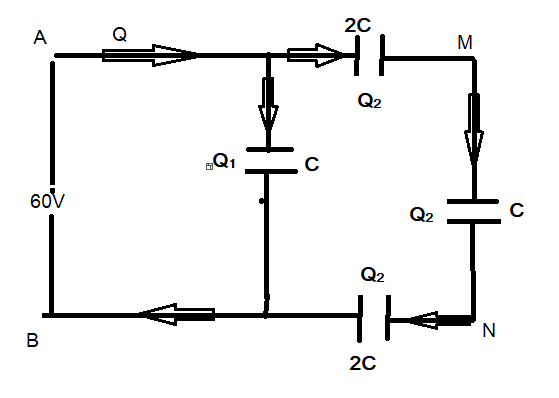
Let Q is the total charge flown from the battery connected.
\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
{} & Q={{C}_{eq}}V \\\
{} & \Rightarrow Q=\left( \dfrac{3C}{2} \right)\left( 60V \right) \\\
{} & \therefore Q=90CV\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } \\\
\end{array}
The total charge gets distributed between the two branches.
Q1+Q2=Q……(i)
As right and the left branches are in parallel, so the electrical potential across both must be the same.
\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
{} & {{V}_{1}}={{V}_{2}} \\\
{} & \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}}{C}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{C}{2} \right)} \\\
{} & \Rightarrow {{Q}_{1}}=2{{Q}_{2}}\left( \dfrac{C}{C} \right) \\\
{} & \therefore {{Q}_{1}}=2{{Q}_{2}}\ldots \ldots \left( ii \right) \\\
\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } & {} \\\
\end{array}
From equations (i) and (ii),
\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
{} & \left( 2{{Q}_{2}} \right)+{{Q}_{2}}=Q \\\
{} & \Rightarrow 3{{Q}_{2}}=Q \\\
{} & \therefore {{Q}_{2}}=\dfrac{Q}{3}\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } \\\
\end{array}
Charge on the capacitor between M and N is Q2
The potential difference between the point M and N is VMN=CQ2
\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } & {{V}_{MN}}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{Q}{3} \right)}{C} \\\
{} & \Rightarrow {{V}_{MN}}=\dfrac{Q}{3C} \\\
\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } & \Rightarrow {{V}_{MN}}=\dfrac{90CV}{3C} \\\
{} & \therefore {{V}_{MN}}=30V\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ }\\!\\!~\\!\\!\text{ } \\\
\end{array}
Hence, the potential difference between M and N is 30V.
Note: The net potential drop in the right loop which comprises the capacitor 2C,C,2C and C. Total charge gets distributed between right and the left branch because they are connected in parallel. The charges on the capacitors in series are the same.
