Question
Question: In the Beta-pleated secondary structure A) Polypeptides show alternate reverse helix B) Two or m...
In the Beta-pleated secondary structure
A) Polypeptides show alternate reverse helix
B) Two or more polypeptides form sheet and run parallel
C) Two or more polypeptides form sheet but the polypeptides run antiparallel
D) Both B and C
Solution
- A polypeptide is a single, long, linear chain of amino acids held together by amide bonds.
- A protein is made up of one or more polypeptides (more than about 50 amino acids long).
- An oligopeptide is made up of only a few amino acids (between two and twenty).
Complete answer:
A few secondary structures are highly stable and are found in abundance in proteins. Secondary configuration refers to the local conformation of a portion of a polypeptide. The alpha-helix and beta conformations are the most common secondary structures.
The beta conformation is a more extended polypeptide chain conformation than the alpha helix. In the beta conformation, the polypeptide chain's backbone is stretched in a zigzag pattern rather than a helical configuration as in the alpha helix. Since the zigzag polypeptide chains are arranged side by side, they form a structure that looks like a sequence of pleats, thus the names beta (pleated) confirmation or beta-sheet. Hydrogen bonds are formed between adjacent segments of polypeptide chains in this process. A beta sheet's neighbouring polypeptide chains may be either parallel (with the same amino-to-carboxyl orientation) or antiparallel (having opposite amino-to-carboxyl orientation).
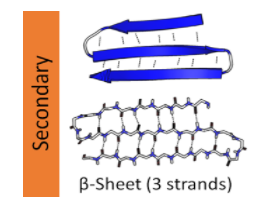
Here, option A is incorrect as we know that In the beta conformation, the polypeptide chain's backbone is stretched in a zigzag pattern rather than a helical configuration as in the alpha helix. Option B is correct as polypeptide can run in any direction. The same applies to option C. Hence, Option D is correct
Note:
- The instructions in mRNA are read during translation, and tRNA transports the proper sequence of amino acids to the ribosome.
- Then, rRNA aids in the formation of bonds between the amino acids, resulting in a polypeptide chain.
- Following the synthesis of a polypeptide chain, it may go through additional processing to shape the finished protein.
