Question
Question: In the adjacent diagram the potential Drop across 3ohm resistor is 
(A)1.0V
(B)1.5V
(C)2V
(D)2.5V
Solution
First, the equivalent resistance has to be calculated. With the value of the resistance, the current of the circuit can be determined using the given voltage. Thereafter, the current passes through the given resistor in the problem. After getting the value of current across the resistor, the potential drop across it can also be found with the help of Ohm’s law.
Formula used:
The equivalent resistance for two series resistors R1 and R2is, R=R1+R2
And, The equivalent resistance for two parallel resistors R1 and R2 is, R=R1+R2R1R2
If the current I is flowing through a resistor R , the potential drop across R is, V=IR (Ohm’s law)
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given circuit is,
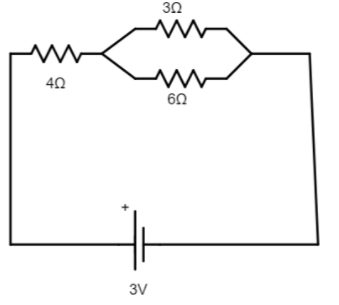
3Ω and 6Ω are in parallel connection, so the equivalent resistance of these two resistors is, R1=3+63×6=2Ω
So the modified circuit will be,
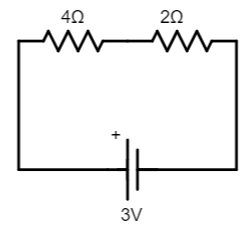
Now, 4Ω and 2Ω are in series connection, so the equivalent resistance of these two resistors is, R2=4+2=6Ω
So, the current passing in the circuit, I=RV , V=3V and R=6Ω
⇒I=63=0.5A
So the current passing through the 3ohmresistor is , I3=I×(6+3)Ω6Ω
⇒I3=0.5×32
⇒I3=0.3333A
Hence the pot. Drop across the 3ohm resistor is, V3=I3×3Ω
⇒V3=0.3333×3
⇒V3=0.999≈1V
Hence the correct option (A)⇒1.0V
Note: We need to know that the potential drop is the difference in electrical charge between two terminals in a circuit represented in volts. the electric potential, potential difference, voltage, potential. electrical phenomenon - a physical phenomenon connecting electricity.
A potential drop in a circuit generally occurs when a current flows through the wire. It is connected to the resistance or impedance to current pass with passive elements in the circuits including wires, contacts, and connectors that affect the level of potential drop.
