Question
Question: In the above compound, how many sites are available for the attack of \( C{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{-}} \) !...
In the above compound, how many sites are available for the attack of CH3O−
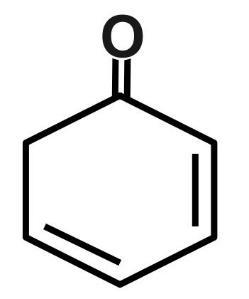
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Solution
We know that the term nucleophile and electrophile were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933. In general, in a group across the periodic table, the more basic the ion, the more reactive it is as a nucleophile. Many different schemes attempting to quantify relative nucleophilic strength have been devised.
Complete answer:
Nucleophilicity, also referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance’s nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophile reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. They may take part in nucleophilic substitution whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge. Nucleophilic describes the affinity of a nucleophile to the positively charged atomic nuclei of atoms. They are a chemical species that donates an electron pair to form a chemical bond in relation to a reaction.
In the reaction both elimination and substitution reaction take place. In the elimination reaction the deprotonation of the carbocation takes place to form alkene, while in the substitution reaction, substitution of the leaving group by a nucleophile takes place. Here substitution takes place at only one position while elimination is taking place at two positions.
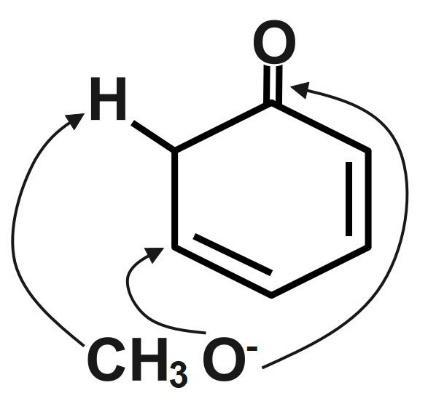
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Remember that the nucleophilicity is decided by the order of basicity. The more basicity means more nucleophilicity. All atoms or ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond tend to act as nucleophiles. Nucleophiles tend to attack substances which have higher electron deficiency.
