Question
Question: In sweet peas, genes C and P are necessary for colour in flowers. The flowers are white in the absen...
In sweet peas, genes C and P are necessary for colour in flowers. The flowers are white in the absence of either or both the genes. What will be the percentage of coloured flowers in the offspring of the cross Ccpp x ccPp?
Solution
The flowers are white or coloured in sweet pea. The C and P genes alone give the flower white colour, e.g., Ccpp, ccPp, cCpp and ccPP. The absence also produces a white colour of both predominant genes (ccpp). On the other side, the floral colour becomes coloured when present together (CCPp, CcPP, CCPP). Consequently, the colour is a product of the two genes' complementary influence.
While talking about the gamete's probabilities,
Ccpp will form Cp and cp
ccPp cP and cp
Complete step by step answer:
In this web lab, students, including Austrian monk Gregor Mendel, experimented with garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) (1822-1884). Mendel wanted to experiment with peas because they possessed four essential qualities:
It was shown that peas were true-breeding (all offspring will have the same characteristic generation after generation).
Peas show a number of contrasting characteristics (purple vs. white flowers; round vs. wrinkled seeds).
Peas typically reproduce by self-pollination, during which eggs within the same flower are fertilized by pollen released by a flower.
Pea plants grow rapidly and do not need a lot of space.
The characteristics which Mendel studied are described below:
Ripe seed shape (R): smooth or wrinkled
Crop albumen (Y) colour (yellow or green)
Flower colour (P) -purple or white
The shape of inflated or constricted ripe pods (I)
The green or yellow colour of unripe pods (G)
Flowers position (A)-axial or terminal
Stem length (T): tall or dwarf
Ccpp X ccPP
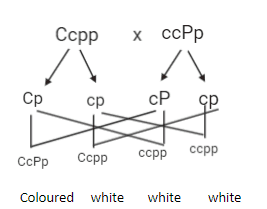
Thus, possible offspring are CcPp (coloured), CcPp (coloured), ccPp (white), ccPp (white).
Hence, the ratio of coloured to white will be 1:1.
The chances are 4: Ccpp (Cp and Cp) and CCPP is formed. Gamete is formed ( cP and cp). 25 of the flowers are therefore coloured.
Hence, 25 is the correct answer.
Note: Pea plants were central to Gregor Mendel's understanding of the means by which the characteristics between parents and offspring are inherited. He chose pea plants because they were easy to grow, were quick to breed and had various observable features including petal and pea.
